A Meta-analysis Comparing External Fixation against Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for the Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures
- PMID: 35990176
- PMCID: PMC9357793
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10080-1557
A Meta-analysis Comparing External Fixation against Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for the Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures
Abstract
Aim: This article aims to compare the outcomes between open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) and external fixation (ExFix) in tibial plateau fractures.
Background: Open reduction and internal fixation and external fixation are common methods for managing tibial plateau fractures without a consensus of choice.
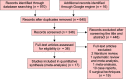
Materials and methods: PubMed, Cochrane Library, Ovid, CINAHL®, Scopus, and Embase were searched. Clinical studies in humans comparing ExFix and ORIF for tibial plateau fractures were included. Case reports, pathological, and biomechanical studies were excluded. Two investigators reviewed the studies independently, and any discrepancies were resolved. The quality and heterogeneity of each study were assessed in addition to calculating the odds ratio (OR) of the surgical outcomes and complications at a 95% confidence interval, with p <0.05 as statistical significance.
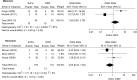
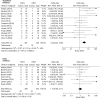
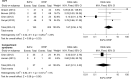
Results: Of the 14 included studies, one was a randomised trial, one was a prospective study, and 12 were retrospective studies. The 865 fractures identified across the studies constituted 458 (52.9%) in the ExFix group and 407 (47.1%) in the ORIF group. Most studies indicated a better outcome for ORIF as compared to ExFix. Open reduction and internal fixation had a lower incidence of superficial infection and postoperative osteoarthritis, while ExFix revealed a lower proportion with heterotopic ossification (HTO).
Conclusion: ExFix has a higher rate of superficial infections and osteoarthritis, whereas ORIF has a higher incidence of HTO. Larger studies are needed to compare outcomes and investigate the findings of this study further.
Clinical significance: This up-to-date meta-analysis on tibial plateau management will help surgeons make evidence-based decisions regarding the use of ORIF versus ExFix.
How to cite this article: Naja AS, Bouji N, Eddine MN, et al. A Meta-analysis Comparing External Fixation against Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for the Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2022;17(2):105-116.
Keywords: External fixator; Fracture; Internal fracture fixation; Tibia.
Copyright © 2022; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures




Similar articles
-
External fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation in the treatment of Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021 Sep;55(5):444-456. doi: 10.5152/j.aott.2021.20350. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021. PMID: 34730533
-
The efficacy of arthroscopy-assisted versus stand-alone open reduction and internal fixation for treating tibial plateau fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 30;25(1):865. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07958-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39472863 Free PMC article.
-
External fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for tibial pilon fractures: A meta-analysis based on observational studies.Chin J Traumatol. 2016 Oct 1;19(5):278-282. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.06.002. Chin J Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 27780508 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopy-Assisted Reduction Percutaneous Internal Fixation Versus Open Reduction Internal Fixation for Tibial Plateau Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Orthop J Sports Med. 2021 Dec 15;9(12):23259671211027838. doi: 10.1177/23259671211027838. eCollection 2021 Dec. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 34938818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of external fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures.Int J Surg. 2017 Mar;39:65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.01.044. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Int J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28089798 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures combined with a proximal fibular and/or posterolateral joint facet fracture on early postoperative functional recovery.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jun 7;18(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03887-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37287007 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of patient factors and procedure on proximal tibia fracture recovery - A retrospective analysis.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Nov;40(10):2281-2286. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.10.9154. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39554646 Free PMC article.
-
The Tibial Plateau fracture-Current incidence and treatment in Germany.PLoS One. 2025 May 9;20(5):e0323443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323443. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40343943 Free PMC article.
-
[Application of reverse traction device in preoperative treatment of high-energy tibial plateau fracture].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jul 15;38(7):830-835. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202404004. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39013820 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Title of the study: finite element analysis of five internal fixation modalities for Schatzker type IV‒C tibial plateau fractures.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 May 23;26(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08770-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40410741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green DP. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

