Advances in Perovskites for Photovoltaic Applications in Space
- PMID: 35990414
- PMCID: PMC9380018
- DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.2c01099
Advances in Perovskites for Photovoltaic Applications in Space
Abstract
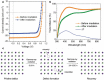
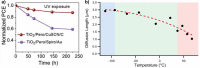
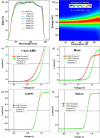
Perovskites have emerged as promising light harvesters in photovoltaics. The resulting solar cells (i) are thin and lightweight, (ii) can be produced through solution processes, (iii) mainly use low-cost raw materials, and (iv) can be flexible. These features make perovskite solar cells intriguing as space technologies; however, the extra-terrestrial environment can easily cause the premature failure of devices. In particular, the presence of high-energy radiation is the most dangerous factor that can damage space technologies. This Review discusses the status and perspectives of perovskite photovoltaics in space applications. The main factors used to describe the space environment are introduced, and the results concerning the radiation hardness of perovskites toward protons, electrons, neutrons, and γ-rays are presented. Emphasis is given to the physicochemical processes underlying radiation damage in such materials. Finally, the potential use of perovskite solar cells in extra-terrestrial conditions is discussed by considering the effects of the space environment on the choice of the architecture and components of the devices.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

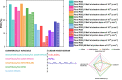
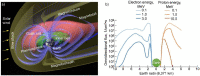


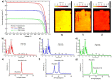


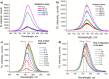


Similar articles
-
Perovskite Solar Cells for Space Applications: Progress and Challenges.Adv Mater. 2021 May;33(21):e2006545. doi: 10.1002/adma.202006545. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 33861877 Review.
-
High-Efficiency Flexible Solar Cells Based on Organometal Halide Perovskites.Adv Mater. 2016 Jun;28(22):4532-40. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504260. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Adv Mater. 2016. PMID: 26669326
-
Highly Stable Inorganic Lead Halide Perovskite toward Efficient Photovoltaics.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Sep 7;54(17):3452-3461. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00343. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34428021
-
Perovskite-inspired materials for photovoltaics and beyond-from design to devices.Nanotechnology. 2021 Mar 26;32(13):132004. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/abcf6d. Nanotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33260167
-
Lead-free hybrid perovskites for photovoltaics.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018 Aug 21;9:2209-2235. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.9.207. eCollection 2018. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30202691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges in the design and synthesis of self-assembling molecules as selective contacts in perovskite solar cells.Chem Sci. 2023 Nov 10;15(5):1534-1556. doi: 10.1039/d3sc04668k. eCollection 2024 Jan 31. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38303950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones H.The recent large reduction in space launch cost. In 48th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2018.
-
- Aerospace Security . Available at https://aerospace.csis.org/data/space-launch-to-low-earth-orbit-how-much... (accessed 2022-05-29).
-
- Hepp A. F.; et al. Ultra-lightweight space power from hybrid thin-film solar cells. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2008, 23, 31–41. 10.1109/MAES.2008.4635069. - DOI
-
- International Space Station. Available at https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/structure/elements/solar_arra... (accessed 2022-05-29).
-
- Yang J.; Bao Q.; Shen L.; Ding L. Potential applications for perovskite solar cells in space. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105019.10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105019. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
