Hearing thresholds elevation and potential association with emotional problems among 1,914 children in Beijing, China
- PMID: 35991012
- PMCID: PMC9386347
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.937301
Hearing thresholds elevation and potential association with emotional problems among 1,914 children in Beijing, China
Abstract
Objectives: School-aged children may experience hearing loss and emotional problems. Previous studies have shown a bidirectional relationship between hearing loss and emotional problems in the elderly population, and we aimed to analyze the association between hearing thresholds and emotional problems in school-aged children.
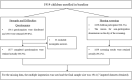
Methods: Based on the Beijing Child Growth and Health Cohort (PROC) study, the hearing screenings were conducted in November 2019 using pure tone audiometry. A total of 1,877 parents completed the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) to assess children's emotional and behavioral status. We used generalized linear regression analysis to assess the potential association of emotional problems with hearing thresholds, based on multiple imputed datasets with a sample size of 1,914.
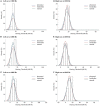
Results: The overall pass rate of hearing screening was 91.5%. The abnormal rate of SDQ total difficulties was 55.8%. Emotional symptoms were positively associated with left ear average hearing thresholds (β = 0.24, 95%CI: 0.08-0.40), and right ear average hearing thresholds (β = 0.18, 95%CI: 0.04-0.32). Conduct problems, hyperactivity/inattention, peer problems, and prosocial behaviors had no association with the pass rate of the hearing screening. Regarding emotional symptoms, boys with many fears and who are easily scared coincided with increased right ear average hearing thresholds (β = 0.67, 95%CI: 0.01-1.33). Girls having many worries, frequently feeling unhappy and downhearted were positively associated with left and right ear average hearing thresholds, respectively (β = 0.96, 95%CI: 0.20-1.73; β = 0.72, 95%CI: 0.07-1.37).
Conclusions: The co-occurrence of hearing problems and emotional problems of children aged 6-8 in Beijing attracts attention. It is important to address undiscovered hearing loss and emotional problems from the perspective of comorbidity driving factors.
Keywords: China; Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ); children; emotional problems; hearing loss; hearing screening; hearing threshold.
Copyright © 2022 Xiao, Amaerjiang, Wang, Li, Zunong, En, Zhao, Wen, Yu, Huang and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between food intake and mental health problems among preschoolers in China.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 19;10:1003416. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1003416. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36339145 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Slight to Mild Hearing Loss With Behavioral Problems and School Performance in Children.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Feb 1;146(2):113-120. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2019.3585. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 31774492 Free PMC article.
-
[The relationship between maternal emotional symptoms during pregnancy and emotional and behavioral problems in preschool children: a birth cohort study].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;50(2):129-35. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.02.006. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26926720 Chinese.
-
Results of the parent-rated Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire in 22,108 primary school students from 8 provinces of China.Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2013 Dec;25(6):364-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0829.2013.06.005. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24991179 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional and behavioral problems in Japanese preschool children with motor coordination difficulties: the role of autistic traits.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022 Jun;31(6):979-990. doi: 10.1007/s00787-021-01732-7. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 33566188
Cited by
-
Newborn hearing screening program in China: a narrative review of the issues in screening and management.Front Pediatr. 2023 Sep 5;11:1222324. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1222324. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37732008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of audiological outcomes of children referred from a universal newborn hearing screening program over 9 years in Beijing, China.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 19;13(1):22630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50171-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38114581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Academy of Audiology: Childhood Hearing Screening Guidelines 2011. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hearingloss/documents/aaa_childhood-hearing-g... (accessed May 22, 2020).
-
- World Health Organization . World Report on Hearing. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2021).

