The cytochrome P450 Cyp6t3 is not required for ecdysone biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 35991292
- PMCID: PMC9386511
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000611
The cytochrome P450 Cyp6t3 is not required for ecdysone biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
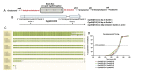
The steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) is essential for proper development and the timing of intermediary stage transitions in insects. As a result, there is intense interest in identifying and defining the roles of the enzymes and signaling pathways that regulate 20E production in the prothoracic gland (PG), the major endocrine organ of juvenile insect phases. Transcriptomics is one powerful tool that has been used to identify novel genes that are up- or down-regulated in the PG which may contribute to 20E regulation. Additional functional characterization of putative regulatory candidate genes typically involves qRT-PCR and/or RNAi mediated knockdown of the candidate mRNA in the PG to assess whether the gene's expression shows temporal regulation in the PG and whether its expression is essential for proper 20E production and the correct timing of developmental transitions. While these methods have proved fruitful for identifying novel regulators of 20E production, characterizing the null phenotype of putative regulatory genes is the gold standard for assigning gene function since RNAi is known to generate various types of "off target" effects. Here we describe the genetic null mutant phenotype of the Drosophila melanogaster Cyp6t3 gene . Cyp6t3 was originally identified as a differentially regulated gene in a PG microarray screen and assigned a place in the "Black Box" step of the E biosynthetic pathway based on RNAi mediated knockdown phenotypes and rescue experiments involving feeding of various intermediate compounds of the E biosynthetic pathway. In contrast, we find that Crispr generated null mutations in Cyp6t3 are viable and have normal developmental timing. Therefore, we conclude that Cyp6t3 is not required for E production under typical lab growth conditions and therefore is not an obligate enzymatic component of the Black Box.
Copyright: © 2022 by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear receptor DHR4 controls the timing of steroid hormone pulses during Drosophila development.PLoS Biol. 2011 Sep;9(9):e1001160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001160. Epub 2011 Sep 27. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21980261 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of candidate intermediates in the Black Box of the ecdysone biosynthetic pathway in Drosophila melanogaster: Evaluation of molting activities on ecdysteroid-defective larvae.J Insect Physiol. 2016 Oct-Nov;93-94:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Insect Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27662806
-
Antagonistic actions of juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone within the ring gland determine developmental transitions in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 2;115(1):139-144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716897115. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29255055 Free PMC article.
-
The Halloween genes code for cytochrome P450 enzymes mediating synthesis of the insect moulting hormone.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Dec;34(Pt 6):1256-60. doi: 10.1042/BST0341256. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 17073797 Review.
-
Rethinking the ecdysteroid source during Drosophila pupal-adult development.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Jan;152:103891. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2022.103891. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36481381 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoreplication in the Drosophila melanogaster prothoracic gland is dispensable for the critical weight checkpoint.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Feb 21;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000741. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000741. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 36908310 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Regulation of Autophagy and Apoptosis in Insects by Sterol Hormone 20-Hydroxyecdysone.Insects. 2023 Nov 12;14(11):871. doi: 10.3390/insects14110871. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37999070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Christesen D, Yang YT, Somers J, Robin C, Sztal T, Batterham P, Perry T. Transcriptome Analysis of Drosophila melanogaster Third Instar Larval Ring Glands Points to Novel Functions and Uncovers a Cytochrome p450 Required for Development. . G3 (Bethesda) 2017 Feb 9;7(2):467–479. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.037333. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chávez VM, Marqués G, Delbecque JP, Kobayashi K, Hollingsworth M, Burr J, Natzle JE, O'Connor MB. The Drosophila disembodied gene controls late embryonic morphogenesis and codes for a cytochrome P450 enzyme that regulates embryonic ecdysone levels. Development. 2000 Oct 1;127(19):4115–4126. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.19.4115. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
