Mammalian derived lipocalin and secretoglobin respiratory allergens strongly bind ligands with potentially immune modulating properties
- PMID: 35991307
- PMCID: PMC9385959
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2022.958711
Mammalian derived lipocalin and secretoglobin respiratory allergens strongly bind ligands with potentially immune modulating properties
Abstract
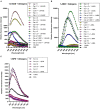
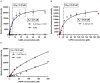
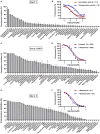
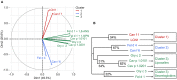
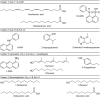
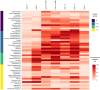
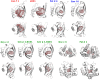
Allergens from furry animals frequently cause sensitization and respiratory allergic diseases. Most relevant mammalian respiratory allergens belong either to the protein family of lipocalins or secretoglobins. Their mechanism of sensitization remains largely unresolved. Mammalian lipocalin and secretoglobin allergens are associated with a function in chemical communication that involves abundant secretion into the environment, high stability and the ability to transport small volatile compounds. These properties are likely to contribute concomitantly to their allergenic potential. In this study, we aim to further elucidate the physiological function of lipocalin and secretoglobin allergens and link it to their sensitizing capacity, by analyzing their ligand-binding characteristics. We produced eight major mammalian respiratory allergens from four pet species in E.coli and compared their ligand-binding affinities to forty-nine ligands of different chemical classes by using a fluorescence-quenching assay. Furthermore, we solved the crystal-structure of the major guinea pig allergen Cav p 1, a typical lipocalin. Recombinant lipocalin and secretoglobin allergens are of high thermal stability with melting temperatures ranging from 65 to 90°C and strongly bind ligands with dissociation constants in the low micromolar range, particularly fatty acids, fatty alcohols and the terpene alcohol farnesol, that are associated with potential semiochemical and/or immune-modulating functions. Through the systematic screening of respiratory mammalian lipocalin and secretoglobin allergens with a large panel of potential ligands, we observed that total amino acid composition, as well as cavity shape and volume direct affinities to ligands of different chemical classes. Therefore, we were able to categorize lipocalin allergens over their ligand-binding profile into three sub-groups of a lipocalin clade that is associated with functions in chemical communication, thus strengthening the function of major mammalian respiratory allergens as semiochemical carriers. The promiscuous binding capability of hydrophobic ligands from environmental sources warrants further investigation regarding their impact on a molecule's allergenicity.
Keywords: Cav p 1 crystal structure; farnesol; fluorescence-quenching assays; lipocalin; mammalian respiratory allergens; protein-ligand interactions; secretoglobin.
Copyright © 2022 Janssen-Weets, Kerff, Swiontek, Kler, Czolk, Revets, Kuehn, Bindslev-Jensen, Ollert and Hilger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhalant Mammal-Derived Lipocalin Allergens and the Innate Immunity.Front Allergy. 2022 Jan 27;2:824736. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2021.824736. eCollection 2021. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35387007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian-derived respiratory allergens - implications for diagnosis and therapy of individuals allergic to furry animals.Methods. 2014 Mar 1;66(1):86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 14. Methods. 2014. PMID: 24041755 Review.
-
Mammalian lipocalin allergens--insights into their enigmatic allergenicity.Clin Exp Allergy. 2012 Apr;42(4):494-504. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03903.x. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012. PMID: 22093088 Review.
-
Component-resolved diagnosis using guinea-pig allergens elucidates allergen sensitization profiles in allergy to furry animals.Clin Exp Allergy. 2021 Jun;51(6):829-835. doi: 10.1111/cea.13873. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Clin Exp Allergy. 2021. PMID: 33797108 Free PMC article.
-
IgE antibodies to animal-derived lipocalin, kallikrein and secretoglobin are markers of bronchial inflammation in severe childhood asthma.Allergy. 2012 May;67(5):661-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2012.02797.x. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Allergy. 2012. PMID: 22339365
Cited by
-
Slowly Making Sense: A Review of the Two-Step Venom System within Slow (Nycticebus spp.) and Pygmy Lorises (Xanthonycticebus spp.).Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 22;15(9):514. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090514. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Semiochemicals Binding to Fel d 1 on Its 3D Conformation and Predicted B-Cell Epitopes Using Computational Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 20;24(14):11685. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411685. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511444 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory frameworks for fragrance safety in cosmetics: a global overview.Toxicol Res. 2025 Mar 1;41(3):199-220. doi: 10.1007/s43188-025-00283-2. eCollection 2025 May. Toxicol Res. 2025. PMID: 40291114 Review.
-
Treatment of Allergies to Fur Animals.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 29;25(13):7218. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137218. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Small Molecule Ligands in IgE-Mediated Allergy.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023 Sep;23(9):497-508. doi: 10.1007/s11882-023-01100-2. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023. PMID: 37351723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haftenberger M, Laussmann D, Ellert U, Kalcklosch M, Langen U, Schlaud M, et al. . Prevalence of sensitisation to aeraoallergens and food allergens: results of the German health interview and examination survey for adults (DEGS1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt GesundheitsforschungGesundheitsschutz. (2013) 56:687–97. 10.1007/s00103-012-1658-1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

