Structure and release properties of pyrethroid/sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin intercalated into layered double hydroxide and layered hydroxide salt
- PMID: 35991605
- PMCID: PMC9388771
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.894386
Structure and release properties of pyrethroid/sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin intercalated into layered double hydroxide and layered hydroxide salt
Abstract
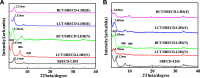
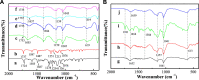
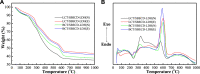
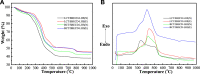
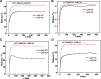
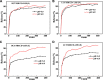
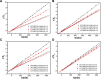
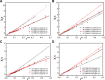
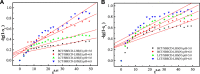
The aim of this study was to realize the intercalation of the pyrethroid pesticides beta-cypermethrin (BCT) and lambda-cyhalothrin (LCT) into ZnAl-layered double hydroxides (LDH) and NiZn-layered hydroxide salt (LHS). BCT (LCT)/SBECD-LDH and BCT (LCT)/SBECD-LHS hybrids were obtained with the aid of sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin (SBECD) through one step method. The hybrids were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and thermogravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TGA/DTA). The hybrids based on LHS had larger basal spacing than those on LDH. The LDH-hybrids prepared in N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) had larger basal spacing than those in ethanol. These results were discussed in terms of the matrix structure and solvent properties. The supramolecular structure of the hybrid was reasonably proposed. Furthermore, the release properties of BCT (LCT) from the hybrids were investigated and discussed in two media. The release rate in pH = 5.0 was slower than that in pH = 6.8. The accumulated release amount of pesticide in pH = 5.0 was lower than that in pH = 6.8. LHS-hybrids synthesized in ethanol exhibit a sustainable release property. These depend on the inclusion complexes' arrangement and release medium. The release kinetic processes could be described by pseudo-second order and parabolic diffusion models. The release behavior can be controlled by adjusting the synthesis conditions and the releasing media. This provides the guidance for the application of SBECD and LDH (LHS) in pesticide formulation.
Keywords: LDH; LHS; SBECD; hybrids; pyrethroid; release behavior.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Liu and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
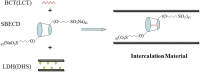
Similar articles
-
DL-mandelic acid intercalated Zn-Al layered double hydroxide: A novel antimicrobial layered material.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 May 1;165:111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 29459259
-
Controlled release of organic-inorganic nanohybrid:cefadroxil intercalated Zn-Al-layered double hydroxide.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 May 29;13:3203-3222. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S138840. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29881273 Free PMC article.
-
The in vitro sustained release profile and antitumor effect of etoposide-layered double hydroxide nanohybrids.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:2053-64. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S43203. Epub 2013 May 24. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23737669 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and release behavior of chlorpyrifos adsolubilized into layered zinc hydroxide nitrate intercalated with dodecylbenzenesulfonate.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Jun 3;7(21):11180-8. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b01068. Epub 2015 May 22. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 25970564
-
The Structure, Preparation, Characterization, and Intercalation Mechanism of Layered Hydroxides Intercalated with Guest Anions.Small. 2023 Oct;19(40):e2300509. doi: 10.1002/smll.202300509. Epub 2023 Jun 4. Small. 2023. PMID: 37271930 Review.
References
-
- Arizaga G., Satyanarayana K., Wypych F. (2007). Layered hydroxide salts: Synthesis, properties and potential applications. Solid State Ionics 178, 1143–1162. 10.1016/j.ssi.2007.04.016 - DOI
-
- Balbino T. A. C., Bellato C. R., da Silva A. D., Neto J. de O. M., Ferreira S. O. (2020). Preparation and evaluation of iron oxide/hydrotalcite intercalated with dodecylsulfate/β-cyclodextrin magnetic organocomposite for phenolic compounds removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 193, 105659. 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105659 - DOI
-
- Bi G., Feng Z. G., Tian S. Z., Cheng J. K. (1995). FT-IR spectra study of photolysis product of pyrethroid. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 12 (6), 39–44.
-
- Biswick T., Park D. H., Choy J. H. (2012). Enhancing the UV A1 screening ability of caffeic acid by encapsulation in layered basic zinc hydroxide matrix. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 73, 1510–1513. 10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.11.039 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

