Injectable click-crosslinked hydrogel containing resveratrol to improve the therapeutic effect in triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 35991627
- PMCID: PMC9386493
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100386
Injectable click-crosslinked hydrogel containing resveratrol to improve the therapeutic effect in triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
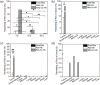
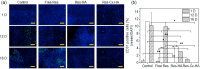
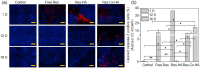
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients are considered intractable, as this disease has few effective treatments and a very poor prognosis even in its early stages. Here, intratumoral therapy with resveratrol (Res), which has anticancer and metastasis inhibitory effects, was proposed for the effective treatment of TNBC. An injectable Res-loaded click-crosslinked hyaluronic acid (Res-Cx-HA) hydrogel was designed and intratumorally injected to generate a Res-Cx-HA depot inside the tumor. The Res-Cx-HA formulation exhibited good injectability into the tumor tissue, quick depot formation inside the tumor, and the depot remained inside the injected tumor for extended periods. In vivo formed Res-Cx-HA depots sustained Res inside the tumor for extended periods. More importantly, the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of Res remained almost exclusively within the tumor and not in other organs. Intratumoral injection of Res-Cx-HA in animal models resulted in significant negative tumor growth rates (i.e., the tumor volume decreased over time) coupled with large apoptotic cells and limited angiogenesis in tumors. Therefore, Res-Cx-HA intratumoral injection is a promising way to treat TNBC patients with high efficacy and minimal adverse effects.
Keywords: Click-crosslinking; Injectable hydrogel; Intratumoral injection; Resveratrol; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
In Vivo Imaging of Click-Crosslinked Hydrogel Depots Following Intratympanic Injection.Materials (Basel). 2020 Jul 9;13(14):3070. doi: 10.3390/ma13143070. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32660032 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable Click-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Depot To Prolong Therapeutic Activity in Articular Joints Affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Jul 17;11(28):24984-24998. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b04979. Epub 2019 Jul 2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31264830
-
An Injectable Click-Crosslinked Hydrogel that Prolongs Dexamethasone Release from Dexamethasone-Loaded Microspheres.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Sep 1;11(9):438. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11090438. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31480552 Free PMC article.
-
An injectable click-crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogel modified with a BMP-2 mimetic peptide as a bone tissue engineering scaffold.Acta Biomater. 2020 Nov;117:108-120. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.09.013. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32927087
-
Nanosoldiers: A promising strategy to combat triple negative breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;110:319-341. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.122. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30529766 Review.
Cited by
-
Amplifying endogenous stem cell migration for in situ bone tissue formation: Substance P analog and BMP mimetic peptide-loaded click-crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogel.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Apr 27;26:101070. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101070. eCollection 2024 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38711939 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Mediated Phenolic Compound Nanodelivery for Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 16;15(6):1751. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061751. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioprinting-By-Design of Hydrogel-Based Biomaterials for In Situ Skin Tissue Engineering.Gels. 2025 Feb 3;11(2):110. doi: 10.3390/gels11020110. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39996653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Resveratrol to Combine with Hydrogel for Photodynamic Therapy against Bacteria and Cancer-A Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 13;12(9):2095. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092095. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol in the Treatment of Gynecological Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(22):4431-4455. doi: 10.2174/0109298673290941240430171146. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38706364 Review.
References
-
- Bianchini G., De Angelis C., Licata L., Gianni L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer - expanded options, evolving needs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022;19(2):91–113. - PubMed
-
- Eskiler G.G., Cecener G., Egeli U., Tunca B. Triple negative breast cancer: new therapeutic approaches and BRCA status. APMIS Suppl. 2018;126(5):371–379. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

