Changes of serofast status in HIV negative asymptomatic neurosyphilis patients after treatment
- PMID: 35991658
- PMCID: PMC9381919
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.938016
Changes of serofast status in HIV negative asymptomatic neurosyphilis patients after treatment
Abstract
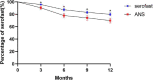
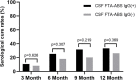
Serofast status after therapy in syphilis patients is a common phenomenon. A proportion of patients who have serofast status exhibit abnormal cerebrospinal fluid test results, which can be defined as asymptomatic neurosyphilis (ANS); however, it remains unclear whether ANS patients can achieve serological cure after anti-neurosyphilis treatment as quickly as other serofast patients. In this study, non-treponemal pallidum antibody serological responses were studied in ANS and serofast control patients, and the cumulative rates of serological cure in the ANS group were 9.6, 22.1, 25.9, and 30.2% in 3, 6, 9, and 12 month after treatment, which were statistically higher than those of the serofast control group. The change gap in serological cure rates was even more pronounced within 6 months after treatment, but the majority of ANS patients had no change in serofast status at 12 months after treatment. Our study indicates that anti-neurosyphilis therapy can partially change the serofast status. As serofast status cannot easily be changed even under neurosyphilis treatment in the majority of patients, the pathogenesis of this condition needs further research.
Keywords: asymptomatic neurosyphilis; serofast; serological cure; syphilis; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhao, Zhou, Yan and Lun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The prevalence of asymptomatic neurosyphilis among HIV-negative serofast patients in China: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 4;15(11):e0241572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241572. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33147295 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of antiretroviral therapy is associated with higher risk of neurosyphilis among HIV-infected patients who remain serofast after therapy for early syphilis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(45):e13171. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013171. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30407349 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of serofast state after treatment for early syphilis in HIV-infected patients.HIV Med. 2021 Mar;22(3):165-171. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12985. Epub 2020 Oct 30. HIV Med. 2021. PMID: 33128333
-
Serofast status in syphilis: Pathogenesis to therapeutics.Clin Chim Acta. 2024 Jun 15;560:119754. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.119754. Epub 2024 May 28. Clin Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38815665 Review.
-
A systematic review of syphilis serological treatment outcomes in HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected persons: rethinking the significance of serological non-responsiveness and the serofast state after therapy.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Oct 28;15:479. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1209-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26511465 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early neurosyphilis with serofast state.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2373305. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2373305. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38922299 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous