Inducible Costimulator-C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 3 Signaling is Involved in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathogenesis
- PMID: 35991707
- PMCID: PMC9386059
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S371801
Inducible Costimulator-C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 3 Signaling is Involved in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: The role of inducible costimulator (ICOS) signaling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has not been fully elucidated.
Methods: We compared the percentages of ICOS+ T cells and ICOS+ regulatory T (Treg) cells in CD4+ T cells and CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ Tregs, respectively, in the peripheral blood of smokers with or without COPD to those in healthy controls. We further characterized their phenotypes using flow cytometry. To investigate the influence of ICOS signaling on C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3) expression in COPD, we evaluated the expression levels of ICOS and CXCR3 in vivo and in vitro.
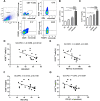
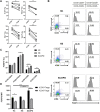
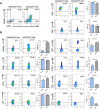
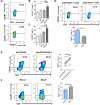
Results: ICOS expression was elevated on peripheral CD4+ T cells and CD4+ Tregs of COPD patients, which positively correlated with the severity of lung function impairment in patients with stable COPD (SCOPD), but not in patients with acute exacerbation of COPD (AECOPD). ICOS+CD4+ Tregs in patients with SCOPD expressed higher levels of coinhibitors, programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), than ICOS-CD4+ Tregs, whereas ICOS+CD4+ T cells mostly exhibited a central memory (CD45RA-CCR7+) or effector memory (CD45RA-CCR7-) phenotype, ensuring their superior potential to respond potently and quickly to pathogen invasion. Furthermore, increased percentages of CXCR3+CD4+ T cells and CXCR3+CD4+ Tregs were observed in the peripheral blood of patients with SCOPD, and the expression level of CXCR3 was higher in ICOS+CD4+ T cells than in ICOS-CD4+ T cells. The percentage of CXCR3+CD4+ T cells was even higher in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid than in matched peripheral blood in SCOPD group. Lastly, in vitro experiments showed that ICOS induced CXCR3 expression on CD4+ T cells.
Conclusions: ICOS signaling is upregulated in COPD, which induces CXCR3 expression. This may contribute to increased numbers of CXCR3+ Th1 cells in the lungs of patients with COPD, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
Keywords: CXCR3; ICOS; T cell; Treg; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
© 2022 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cigarette smoking promotes inflammation in patients with COPD by affecting the polarization and survival of Th/Tregs through up-regulation of muscarinic receptor 3 and 5 expression.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 6;9(11):e112350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112350. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25375131 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Imbalance between Subpopulations of Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of COPD.COPD. 2017 Dec;14(6):618-625. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2017.1385055. Epub 2017 Nov 22. COPD. 2017. PMID: 29166179
-
Th1-Like ICOS+ Foxp3+ Treg Cells Preferentially Express CXCR3 and Home to β-Islets during Pre-Diabetes in BDC2.5 NOD Mice.PLoS One. 2015 May 6;10(5):e0126311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126311. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25946021 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells in the blood of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A systematic review and meta-analysis.Respir Med. 2025 Jun;242:108104. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2025.108104. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Respir Med. 2025. PMID: 40246247
-
The functions of CD4 T-helper lymphocytes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Jan 25;54(2):173-178. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2021009. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 35130627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

