Acute Dose-Response of Duration During the Isometric Forearm Plank Exercise on Muscle Thickness, Echo-Intensity, Peak Force, and Perception of Effort in Recreationally-Trained Participants
- PMID: 35991937
- PMCID: PMC9365105
- DOI: 10.70252/RDKT2873
Acute Dose-Response of Duration During the Isometric Forearm Plank Exercise on Muscle Thickness, Echo-Intensity, Peak Force, and Perception of Effort in Recreationally-Trained Participants
Abstract
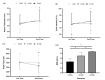
The primary purpose of this study was to evaluate the acute effects of different durations of the isometric forearm plank exercise (IFPE) on peak force, echo intensity, muscle thickness, and perception of effort in recreationally-trained participants. Fifteen resistance-trained participants (23±3years, 76.4±6.5kg, 173.3±6.5cm) performed the IFPE with bodyweight in one of three durations in a randomized order: a). 1-min, b). 2-min, and c). 3-min. Muscle thickness (MT), echo intensity (EI), peak force (PF), and rating of perceived exertion (RPE) were measured pre-test and post-test. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVAs (2×3) were used to test differences between tests (pre-test and post-test) and treatment (1-min, 2-min, and 3-min) for PF, MT, and EI. One-way ANOVA was used to compare RPE between treatments (1-min, 2-min, and 3- min). There was a significant increase between pre- and post-test only for 3-min IFPE (p=0.008). For EI, there was a significant increase between pre- and post-test only for 3-min IFPE (p<0.001). For PF, there were observed significant reductions on post-test between 1-min vs. 3-min (p<0.001) and 2-min vs. 3-min IFPE (p<0.001). For RPE, there were statistical differences between 1-min vs. 2-min (p<0.001), 1-min and 3-min (p<0.001), 2-min and 3-min (p=0.001). In conclusion, only 3-min IFPE induced an increase in MT and EI and a reduction in PF when compared to 1-min and 2-min (during the post-test). RPE increased with the increase in the duration of the IFPE.
Keywords: Isometric contraction; muscle pump; performance; strength.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Muscle Thickness, Echo-Intensity, Peak Force, Time Under Tension, Total Load Lifted, and Perception of Effort Comparisons Between Two Abdominal Crunch Resistance Training Protocols in Recreationally-Trained Participants.Int J Exerc Sci. 2023 May 1;16(6):538-549. doi: 10.70252/BCSY3591. eCollection 2023. Int J Exerc Sci. 2023. PMID: 37621710 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Variability Did Not Affect Muscle Thickness and Peak Force for Elbow Flexors After a Resistance Training Session in Recreationally-Trained Subjects.Int J Exerc Sci. 2021 Nov 1;14(3):1294-1304. doi: 10.70252/XAFX1170. eCollection 2021. Int J Exerc Sci. 2021. PMID: 35096238 Free PMC article.
-
Seated row and biceps curl exercises present similar acute responses on muscle thickness, arm circumference, and peak force for elbow flexors after a resistance training session in recreationally-trained subjects.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020 Nov;60(11):1415-1422. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.20.10996-4. Epub 2020 Jun 23. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020. PMID: 32586082
-
An examination of changes in skeletal muscle thickness, echo intensity, strength and soreness following resistance exercise.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2020 Jul;40(4):238-244. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12630. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32187417
-
Convergent Validity of Ratings of Perceived Exertion During Resistance Exercise in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med Open. 2022 Jan 8;8(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40798-021-00386-8. Sports Med Open. 2022. PMID: 35000021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Deep Core Muscle System Training Through Virtual Reality on Selected Posturographic Parameters.J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025 May 21;10(2):185. doi: 10.3390/jfmk10020185. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025. PMID: 40407469 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Adaptations in the Gastrocnemius Muscle from an Exercise Program with and without Low-Intensity Blood Flow Restriction Banding in 18 Male Amateur Basketball Players Aged 16-45 Years.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jul 14;30:e944627. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944627. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39003516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfuth M, Cornely D. Chronic low back pain: Comparison of mobilization and core stability exercises. Orthopade. 2016;45(7):579–590. - PubMed
-
- Balshaw T, Massey GJ, Maden-Wilkinson TM, Tillin NA, Folland JP. Training-specific functional, neural, and hypertrophic adaptations to explosive- vs. sustained-contraction strength training. J Appl Physiol. 2016;120(11):1364–1373. - PubMed
-
- Bigland-Ritchie B, Jones DA, Hosking GP, Edwards RH. Central and peripheral fatigue in sustained maximum voluntary contractions of human quadriceps muscle. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1978;54(6):609–614. - PubMed
-
- Chen YL, Wolin MS, Messina EJ. Evidence for cgmp mediation of skeletal muscle arteriolar dilation to lactate. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81(1):349–354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
