Borrelia burgdorferi modulates the physical forces and immunity signaling in endothelial cells
- PMID: 35992087
- PMCID: PMC9389243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104793
Borrelia burgdorferi modulates the physical forces and immunity signaling in endothelial cells
Abstract
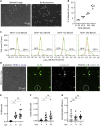
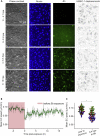
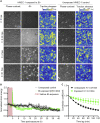
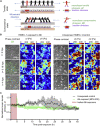
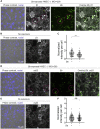
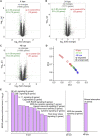
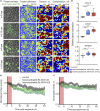
Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), a vector-borne bacterial pathogen and the causative agent of Lyme disease, can spread to distant tissues in the human host by traveling in and through monolayers of endothelial cells (ECs) lining the vasculature. To examine whether Bb alters the physical forces of ECs to promote its dissemination, we exposed ECs to Bb and observed a sharp and transient increase in EC traction and intercellular forces, followed by a prolonged decrease in EC motility and physical forces. All variables returned to baseline at 24 h after exposure. RNA sequencing analysis revealed an upregulation of innate immune signaling pathways during early but not late Bb exposure. Exposure of ECs to heat-inactivated Bb recapitulated only the early weakening of EC mechanotransduction. The differential responses to live versus heat-inactivated Bb indicate a tight interplay between innate immune signaling and physical forces in host ECs and suggest their active modulation by Bb.
Keywords: Biophysics; Cell biology; Immunology; Microbiology; Transcriptomics.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- CDC Lyme Disease. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/index.html.
-
- Alban P.S., Johnson P.W., Nelson D.R. Serum-starvation-induced changes in protein synthesis and morphology of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiology (Read.) 2000;146:119–127. - PubMed
-
- Anderson G.G., Palermo J.J., Schilling J.D., Roth R., Heuser J., Hultgren S.J. Intracellular bacterial biofilm-like pods in urinary tract infections. Science. 2003;301:105–107. - PubMed
-
- Barakat A., Lieu D. Differential responsiveness of vascular endothelial cells to different types of fluid mechanical shear stress. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2003;38:323–343. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

