Regulation of the kiss2 promoter in yellowtail clownfish (Amphiprion clarkii) by cortisol via GRE-dependent GR pathway
- PMID: 35992144
- PMCID: PMC9382246
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.902737
Regulation of the kiss2 promoter in yellowtail clownfish (Amphiprion clarkii) by cortisol via GRE-dependent GR pathway
Abstract
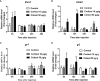
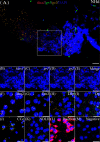
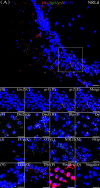
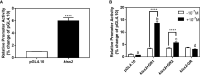
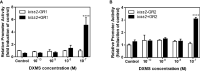
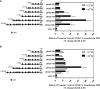
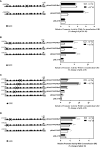
Kisspeptin plays a vital role in mediating the stress-induced reproductive regulation. Cortisol, known as a stress-related hormone, is involved in gonadal development and sexual differentiation by binding with glucocorticoid receptor (GR) to regulate the expression of kiss gene. In the present study, cortisol treatment in yellowtail clownfish (Amphiprion clarkii) showed that the expression of kiss (kiss1 and kiss2) and gr (gr1 and gr2) genes were increased significantly. We demonstrated that the yellowtail clownfish Kiss neurons co-express the glucocorticoid receptors in the telencephalon, mesencephalon, cerebellum, and hypothalamus. We further cloned the promoter of kiss2 gene in yellowtail clownfish and identified the presence of putative binding sites for glucocorticoid receptors, estrogen receptors, androgen receptors, progesterone receptors, AP1, and C/EBP. Applying transient transfection in HEK293T cells of the yellowtail clownfish kiss2 promoter, cortisol (dexamethasone) treatment was shown to enhance the promoter activities of the yellowtail clownfish kiss2 gene in the presence of GRs. Deletion analysis of kiss2 promoter indicated that cortisol-induced promoter activities were located between position -660 and -433 with GR1, and -912 and -775 with GR2, respectively. Finally, point mutation studies on the kiss2 promoter showed that cortisol-stimulated promoter activity was mediated by one GRE site located at position -573 in the presence of GR1 and by each GRE site located at position -883, -860, -851, and -843 in the presence of GR2. Results of the present study provide novel evidence that cortisol could regulate the transcription of kiss2 gene in the yellowtail clownfish via GRE-dependent GR pathway.
Keywords: Amphiprion clarkii; cortisol; glucocorticoid receptor; kiss2 promoter; stress.
Copyright © 2022 Bu, Zhang, Zhang, Li, Zheng, Huang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

