Post-Exercise Arterial Stiffness Responses Are Similar After Acute Eccentric and Concentric Arm Cycling
- PMID: 35992180
- PMCID: PMC9362888
- DOI: 10.70252/CRLE3385
Post-Exercise Arterial Stiffness Responses Are Similar After Acute Eccentric and Concentric Arm Cycling
Abstract
Upper-body resistance exercise effectively increases muscular strength, but may concomitantly increase arterial stiffness. Eccentric exercise can lead to muscle soreness and arterial stiffness in untrained participants. However, it is unclear if upper-body eccentric exercise could reduce arterial stiffness in a single session for participants that have undergone progressive training. Our purpose was to compare acute responses to upper-body eccentric (novel, ECCarm) and concentric (traditional, CONarm) steady state arm cycling. We hypothesized that arm arterial stiffness would be reduced after both ECCarm and CONarm. Twenty-two young healthy individuals performed either ECCarm (n = 11) or CONarm (n = 11) at ~70% of peak heart rate for 20 min after a training period. Heart rate, central pulse wave velocity (cPWV), and peripheral pulse wave velocity (pPWV; i.e., arm arterial stiffness) were assessed before, 10 min, and 30 min after exercise. Heart rate was not elevated at 10 min post ECCarm, but was elevated at 10- and 30-min post CONarm (p < 0.01). After exercise, pPWV was decreased at 10 min post for both ECCarm (7.1 ± 0.3 vs. 6.5 ± 0.2 m/s) and CONarm (7.0 ± 0.2 vs. 6.5 ± 0.2 m/s; p < 0.05), while both groups returned to baseline values 30 min post. cPWV did not change in either group. Our results indicate that acute ECCarm provides a high-force, low energy cost form of resistance exercise that acutely reduces arm arterial stiffness. The reduction in pPWV and rapid heart rate recovery suggests that ECCarm is a safe form of exercise for overall and cardiovascular health.
Keywords: Arm ergometry; eccentric exercise; pulse wave velocity; steady state exercise.
Figures

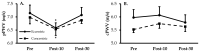
References
-
- Abbiss CR, Quod MJ, Levin G, Martin DT, Laursen PB. Accuracy of the Velotron ergometer and SRM power meter. Int J Sports Med. 2009;30(2):107–112. - PubMed
-
- Anton D, Mizner RL, Hess JA. The effect of lift teams on kinematics and muscle activity of the upper extremity and trunk in bricklayers. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013;43(4):232–241. - PubMed
-
- Augustine JA, Yoon ES, Choo J, Heffernan KS, Jae SY. The relationship between cardiorespiratory fitness and aortic stiffness in women with central obesity. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2016;25(7):680–686. - PubMed
-
- Barnes JN, Trombold JR, Dhindsa M, Lin HF, Tanaka H. Arterial stiffening following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. J Appl Physiol. 1985;2010;109(4):1102–1108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
