Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and factors associated with oxygen therapy for critically ill patients among nurses at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital Northwest, Ethiopia, 2021
- PMID: 35992207
- PMCID: PMC9389197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104334
Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and factors associated with oxygen therapy for critically ill patients among nurses at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital Northwest, Ethiopia, 2021
Abstract
Background: Administering oxygen therapy has an essential role in preventing and managing hypoxemia in both acute and chronic conditions. The aim of this study was to assess knowledge, attitude and factors associated with oxygen therapy for critically ill patients among nurses.
Methods: An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted from May 23 to June 07 at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia, in 2021. A self-administered, structured and validated questionnaire was used. It has socio-demographic characteristics, multiple choice questions, items that measure the possible associated factors and items that were used to assess the level of knowledge and attitude. Epi Data ("The EpiData Association" Odense, Denmark) version 4.6 was used to enter data, and SPSS (IBM) version 20 was used to analyze it. Both bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify associated factors. Variables with a p value < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
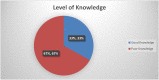
Results: The overall proportion of critically ill patients with good knowledge and a positive attitude toward oxygen therapy was 33% (95% CI: 25.8-37.8) and 53.8% (95% CI: 49-59), respectively. Age (AOR; 1.738, 95% CI: 1.034-2.921), level of education (AOR; 7.731, 95% CI: 2.507-23.846) and guideline (AOR; 4.338, 95% CI: 2.233-8.428) and good level of practice (AOR; 1.885, 95% CI: 1.173-3.030) were discovered to be significant factors associated with good knowledge towards oxygen therapy and the reading guideline was found to be a significant factor associated with a positive attitude toward oxygen therapy (AOR; 1.396, 95% CI: 0.830-2.348).
Conclusions: and recommendations: The level of knowledge was low, whereas the attitude of nurses was positive towards oxygen therapy. Reading guidelines, older aged nurses, master holder nurses, and good practice were significant factors associated with good knowledge of oxygen therapy, and reading guidelines was statistically associated with a positive attitude toward oxygen therapy. Thus, nurses need to be aware and skillful regarding the updated oxygen therapy guidelines. They should improve their level of education.
Keywords: Attitude; Inhalation oxygen therapy; Knowledge; Northwest Ethiopia; Nurse; Practice.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of practice and barriers of oxygen therapy in critically ill patients among nurses: A survey from University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital Northwest, Ethiopia, 2021.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Mar 14;76:103481. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103481. eCollection 2022 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35313541 Free PMC article.
-
Work experience was associated with the knowledge and practice of catheter-associated urinary tract infection prevention among nurses at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, northwest Ethiopia, 2021.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Jan 30;23(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02176-8. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 36717910 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with knowledge and attitude towards adult cardiopulmonary resuscitation among healthcare professionals at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: an institutional-based cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2020 Sep 28;10(9):e037416. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037416. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32988946 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitude, and associated factors toward pediatric pain management among nurses at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: A cross-sectional study.SAGE Open Med. 2022 Feb 7;10:20503121221075163. doi: 10.1177/20503121221075163. eCollection 2022. SAGE Open Med. 2022. PMID: 35154739 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of knowledge and attitude of pregnant women towards antenatal ultrasound in University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital at antenatal care clinic, Northwest Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 8;18(11):e0292496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292496. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37939118 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Knowledge, attitude, practice and associated factors of oxygen therapy among health professionals in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0309823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309823. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knight A.R., et al. Understanding the effects of oxygen administration in haemorrhagic shock. Nurs. Crit. Care. 2011;16(1):28–35. - PubMed
-
- Organization W.H. WHO; Geneva: 2016. Essential Medicines and Health Products: WHO MODEL Lists of Essential Medicines; pp. 33–47.
-
- Hatipoğlu U., Stoller J.K. Supplemental oxygen in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence from nocturnal oxygen treatment trial to long-term oxygen treatment trial. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018;24(2):179–186. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources