Quartz crystal microbalance and atomic force microscopy to characterize mimetic systems based on supported lipids bilayer
- PMID: 35992275
- PMCID: PMC9382308
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.935376
Quartz crystal microbalance and atomic force microscopy to characterize mimetic systems based on supported lipids bilayer
Abstract
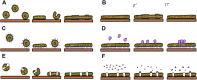
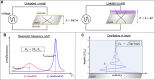
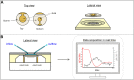
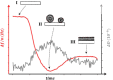
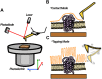
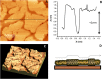
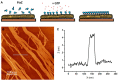
Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) with dissipation and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) are two characterization techniques that allow describing processes taking place at solid-liquid interfaces. Both are label-free and, when used in combination, provide kinetic, thermodynamic and structural information at the nanometer scale of events taking place at surfaces. Here we describe the basic operation principles of both techniques, addressing a non-specialized audience, and provide some examples of their use for describing biological events taking place at supported lipid bilayers (SLBs). The aim is to illustrate current strengths and limitations of the techniques and to show their potential as biophysical characterization techniques.
Keywords: atomic force microscopy; biomimetic membranes; label-free detection; quartz crystal microbalance; supported lipid bilayers.
Copyright © 2022 Bonet, Cava and Vélez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell adhesion on supported lipid bilayers functionalized with RGD peptides monitored by using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014 Apr 1;116:459-64. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.01.032. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014. PMID: 24552662
-
Electrodeless QCM-D for lipid bilayer applications.Biosens Bioelectron. 2011 Jan 15;26(5):1833-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.01.018. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011. PMID: 20153163
-
Formation of a Fully Anionic Supported Lipid Bilayer to Model Bacterial Inner Membrane for QCM-D Studies.Membranes (Basel). 2022 May 27;12(6):558. doi: 10.3390/membranes12060558. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736265 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Interaction between Nanoparticles and Lipid Membranes by Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring.Front Chem. 2016 Dec 5;4:46. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2016.00046. eCollection 2016. Front Chem. 2016. PMID: 27995125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid bilayers: Phase behavior and nanomechanics.Curr Top Membr. 2020;86:1-55. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Curr Top Membr. 2020. PMID: 33837691 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-free expression with a quartz crystal microbalance enables rapid, dynamic, and label-free characterization of membrane-interacting proteins.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 17;7(1):1005. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06690-9. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39152195 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction Mechanisms and Predictions of the Biofouling of Polymer Films: A Combined Atomic Force Microscopy and Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring Study.Langmuir. 2023 May 9;39(18):6592-6612. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00587. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Langmuir. 2023. PMID: 37104647 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term effects of sweetened acidic beverages consumption on human saliva: Colloidal properties and protein composition.PLoS One. 2025 Sep 3;20(9):e0330023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330023. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40901782 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

