Iatrogenic Injury to the Suprascapular Nerve Following Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- PMID: 35992510
- PMCID: PMC9386855
- DOI: 10.1177/24715492221103518
Iatrogenic Injury to the Suprascapular Nerve Following Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Case Report
Abstract
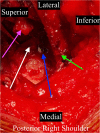
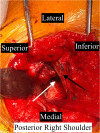
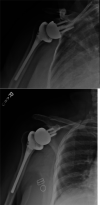
The location and course of the suprascapular nerve (SSN) to the glenohumeral joint places this nerve at risk when operating around the shoulder. Iatrogenic injury to the suprascapular nerve has been described in several different procedures including, rotator cuff repairs, posterior capsulorraphy, Bankart repairs, SLAP lesion repairs, Latarjet procedures, and shoulder arthroplasty. We present a case of iatrogenic suprascapular nerve injury due to superior glenoid baseplate screw placement following primary reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA), a novel approach to diagnosis of nerve injury, and treatment.
Keywords: arthroplasty; revision; shoulder.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

