Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer biomarkers beyond morphology
- PMID: 35992775
- PMCID: PMC9382689
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.947446
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer biomarkers beyond morphology
Abstract
Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) still represents a challenge in decision-making and clinical management since prognostic and predictive biomarkers of response to treatment are still under investigation. In addition to the risk factors defined by EORTC guidelines, histological features have also been considered key variables able to impact on recurrence and progression in bladder cancer. Conversely, the role of genomic rearrangements or expression of specific proteins at tissue level need further assessment in NMIBC. As with muscle-invasive cancer, NMIBC is a heterogeneous disease, characterized by genomic instability, varying rates of mutation and a wide range of protein tissue expression. In this Review, we summarized the recent evidence on prognostic and predictive tissue biomarkers in NMIBC, beyond morphological parameters, outlining how they could affect tumor biology and consequently its behavior during clinical care. Our aim was to facilitate clinical evaluation of promising biomarkers that may be employed to better stratify patients. We described the most common molecular events and immunohistochemical protein expressions linked to recurrence and progression. Moreover, we discussed the link between available treatments and molecular drivers that could be predictive of clinical response. In conclusion, we foster further investigations with particular focus on immunohistochemical evaluation of tissue biomarkers, a promising and cost-effective tool for daily practice.
Keywords: BCG response; biomarker; bladder cancer; molecular subtypes; non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; predictive; prognostic.
Copyright © 2022 De Carlo, Valeri, Corbitt, Cieri and Colombo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

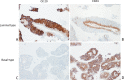
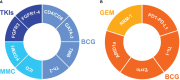
References
-
- IARC Publications . WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and Male genital organs – IARC (2022). Available at: https://www.iarc.who.int/news-events/iarc-publications-who-classificatio....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

