Metastases to the thyroid gland: ultrasonographic findings and diagnostic value of fine-needle aspiration cytology
- PMID: 35992787
- PMCID: PMC9381705
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939965
Metastases to the thyroid gland: ultrasonographic findings and diagnostic value of fine-needle aspiration cytology
Abstract
Introduction: In the present study, we aimed to analyze ultrasonographic findings of metastases to the thyroid and explore the role of fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the diagnosis of metastases to the thyroid.
Methods: Twelve cases of cytologically or/and pathologically confirmed metastatic tumors of the thyroid gland were reviewed. All the primary thyroid lesions and lymphomas were excluded. The location, maximum size, echogenicity, shape, margin, presence of calcifications, vascularity, and cervical lymph nodes were assessed on ultrasonography. In addition, the results of cytology or pathology (or both) were noted retrospectively.
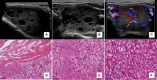
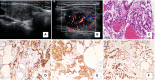
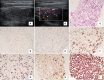
Results: Eight of 10 patients were diagnosed correctly with FNAC. Two cases presented with diffuse involvement in both thyroid lobes. Nine cases demonstrated a hypoechoic nodule with an irregular margin, four of which had microcalcifications. One case presented with a mixed solid and cystic mass with an oval shape. The lesions with cervical lymph nodes were found in seven cases.
Conclusion: Most metastatic thyroid cancer has similar ultrasound features to primary thyroid cancer. In some cases with atypical US features, ultrasound diagnosis should be combined with the medical history. FNAC might be helpful in the diagnosis.
Keywords: fine-needle aspiration cytology; metastasis to the thyroid gland; secondary thyroid neoplasm; thyroid; thyroid metastasis; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Gao, Wang, Zhang, Zhan and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

