Measurement tools to assess activities of daily living in patients with Parkinson's disease: A systematic review
- PMID: 35992900
- PMCID: PMC9386643
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.945398
Measurement tools to assess activities of daily living in patients with Parkinson's disease: A systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Parkinson's disease (PD) is associated with a progressive inability to accomplish essential activities of daily living (ADL) resulting in a loss of autonomy and quality of life. Accurate measurement of ADL in PD is important to monitor disease progression and optimize care. Despite its relevance, it is still unclear which measurement instruments are the most suitable for evaluating ADL in people with PD.
Objective: To identify and critically appraise which measurement instruments have been used to assess ADL in PD.
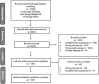
Methods: A systematic review was conducted using the databases CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and PEDro from their inception to October 2021 to identify all observational and experimental studies conducted in PD or atypical parkinsonism that included an ADL assessment. Titles and abstracts were screened independently by two authors. The clinimetric properties of the measurement instruments were assessed, and the instruments were classified as "recommended," "suggested," or "listed."
Results: A total of 129 articles were included, with 37 measurement instruments used. The Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), the Schwab & England ADL scale (S&E scale), the Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS), the Barthel Index, the Lawton-Brody Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Scale, the Functional Independence Measure (FIM) and the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study - ADL (ADCS-ADL) scale were the seven most frequently cited measurement instruments. Of these, only two included an assessment of basic and instrumental ADL.
Conclusion: MDS-UPDRS and the S&E scale were the only two scales that could be classified as recommended. For the MDS-UPDRS, either the full version or only Part II, which is focused on ADL, can be used. Future studies should explore the use of wearable devices to assess ADL remotely and more continuously.
Keywords: ADL; Movement disorders; activities of daily living; assessment; clinical scales; measurement tools; outcome measures; patients reported outcomes.
Copyright © 2022 Bouça-Machado, Fernandes, Ranzato, Beneby, Nzwalo and Ferreira.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous