Brain alterations of regional homogeneity, degree centrality, and functional connectivity in vulnerable carotid plaque patients with neither clinical symptoms nor routine MRI lesions: A resting-state fMRI study
- PMID: 35992918
- PMCID: PMC9389209
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.937245
Brain alterations of regional homogeneity, degree centrality, and functional connectivity in vulnerable carotid plaque patients with neither clinical symptoms nor routine MRI lesions: A resting-state fMRI study
Abstract
Aims: Based on resting-state functional MRI (fMRI), we preliminarily explored brain alterations in asymptomatic patients with vulnerable carotid plaques, but carotid stenosis was < 50%.
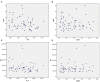
Methods: A total of 58 asymptomatic patients with vulnerable carotid plaques (stenosis <50%) and 38 healthy controls were recruited. Between-group differences in regional homogeneity (ReHo), degree centrality (DC), and functional connectivity (FC) were analyzed. Correlation analysis was performed between the ReHo or DC values in altered brain regions as well as voxel-wise abnormal FC and scores on neuropsychiatric scales, serum interleukin-6 (IL-6), and C-reactive protein (CRP).
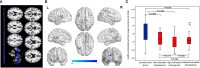
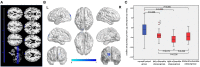
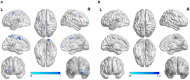
Results: Both ReHo and DC values on the left superior occipital gyrus (SOG.L) of the asymptomatic vulnerable carotid plaque group reduced, regardless of plaque location (left, right, or bilateral). Functional connections weakened between the SOG.L and right lingual gyrus (LING.R)/right inferior occipital gyrus (IOG.R), right middle frontal gyrus (MFG.R)/orbital part of superior frontal gyrus (ORBsup.R)/orbital part of middle frontal gyrus (ORBmid.R), left precentral gyrus (PreCG.L)/postcentral gyrus (PoCG.L), left supplementary motor area (SMA.L), right paracentral lobule (PCL.R), left precuneus (PCUN.L), and right postcentral gyrus (PoCG.R)/PCL.R. In ReHo-altered brain regions, ReHo values were positively correlated with Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAMD) scores, and the setting region of abnormal ReHo as seed points, voxel-wise FC between the SOG.L and PreCG.L was negatively correlated with CRP.
Conclusions: Cerebral alterations of neuronal synchronization, activity, and connectivity properties in the asymptomatic vulnerable carotid plaque group were independent of the laterality of vulnerable carotid plaques. Significant relation between ReHo values on the SOG.L and HAMD indicated that even when there were neither clinical symptoms nor lesions on routine MRI, brain function might have changed already at an early stage of carotid atherosclerosis. Inflammation might play a role in linking vulnerable carotid plaques and changes of resting-state functional connectivity.
Keywords: carotid plaque; degree centrality; regional homogeneity; resting-state fMRI; vulnerable plaque.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Xing, Ouyang, Li, Jin and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered regional homogeneity and functional connectivity of brain activity in young HIV-infected patients with asymptomatic neurocognitive impairment.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 10;13:982520. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.982520. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36303561 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant brain voxel-wise resting state fMRI in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.J Neuroimaging. 2021 Jul;31(4):773-783. doi: 10.1111/jon.12858. Epub 2021 Apr 5. J Neuroimaging. 2021. PMID: 33817897
-
Altered Static and Dynamic Voxel-mirrored Homotopic Connectivity in Patients with Frontal Glioma.Neuroscience. 2022 May 10;490:79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.006. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35278629
-
Alterations in degree centrality and functional connectivity in tension-type headache: a resting-state fMRI study.Brain Imaging Behav. 2024 Aug;18(4):819-829. doi: 10.1007/s11682-024-00875-w. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Brain Imaging Behav. 2024. PMID: 38512647 Review.
-
Abnormalities of brain structure and function in cervical spondylosis: a multi-modal voxel-based meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 14;18:1415411. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1415411. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38948928 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Abnormalities of regional brain activity in patients with asymptomatic internal carotid artery occlusion: a resting-state fMRI study.BMC Neurol. 2025 Apr 25;25(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04156-x. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40281414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buckner R. L., Sepulcre J., Talukdar T., Krienen F. M., Liu H., Hedden T., et al. . (2009). Cortical hubs revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity: mapping, assessment of stability, and relation to Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 29, 1860–1873. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5062-08.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

