Reproducibility of chestwall and heart position using surface-guided versus RPM-guided DIBH radiotherapy for left breast cancer
- PMID: 35993318
- PMCID: PMC9859984
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13755
Reproducibility of chestwall and heart position using surface-guided versus RPM-guided DIBH radiotherapy for left breast cancer
Abstract
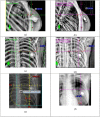
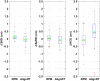
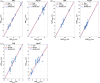
This study compared the reproducibility of chestwall and heart position using surface-guided versus RPM (real-time position management)-guided deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH) radiotherapy for left sided breast cancer. Forty DIBH patients under either surface-guided radiotherapy (SGRT) or RPM guidance were studied. For patients treated with tangential fields, reproducibility was measured as the displacements in central lung distance (CLD) and heart shadow to field edge distance (HFD) between pretreatment MV (megavoltage) images and planning DRRs (digitally reconstructed radiographs). For patients treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT), sternum to isocenter (ISO) distance (StID), spine to rib edge distance (SpRD), and heart shadow to central axis (CAX) distance (HCD) between pretreatment kV images and planning DRRs were measured. These displacements were compared between SGRT and RPM-guided DIBH. In tangential patients, the mean absolute displacements of SGRT versus RPM guidance were 0.19 versus 0.23 cm in CLD, and 0.33 versus 0.62 cm in HFD. With respect to planning DRR, heart appeared closer to the field edge by 0.04 cm with surface imaging versus 0.62 cm with RPM. In VMAT patients, the displacements of surface imaging versus RPM guidance were 0.21 versus 0.15 cm in StID, 0.24 versus 0.19 cm in SpRD, and 0.72 versus 0.41 cm in HCD. Heart appeared 0.41 cm further away from CAX with surface imaging, whereas 0.10 cm closer to field CAX with RPM. None of the differences between surface imaging and RPM guidance was statistically significant. In conclusion, the displacements of chestwall were small and were comparable with SGRT- or RPM-guided DIBH. The position deviations of heart were larger than those of chestwall with SGRT or RPM. Although none of the differences between SGRT and RPM guidance were statistically significant, there was a trend that the position deviations of heart were smaller and more favorable with SGRT than with RPM guidance in tangential patients.
Keywords: breast cancer; comparison; deep inspiration breath hold; real-time position management; surface imaging.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accuracy and potential improvements of surface-guided breast cancer radiotherapy in deep inspiration breath-hold with daily image-guidance.Phys Med Biol. 2022 Sep 26;67(19). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac9109. Phys Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36084626
-
Setup margins based on the inter- and intrafractional setup error of left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy using deep inspiration breath-hold technique (DIBH) and surface guided radiotherapy (SGRT).J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jun;25(6):e14271. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14271. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38273673 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of deep inspiration breath hold, surface-guided radiotherapy, and daily CBCT on the organs at risk in breast cancer radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27814. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77482-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537683 Free PMC article.
-
Review of clinical applications and challenges with surface-guided radiation therapy.J Cancer Res Ther. 2023 Jul-Sep;19(5):1160-1169. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1147_21. J Cancer Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37787279 Review.
-
Advances and potential of optical surface imaging in radiotherapy.Phys Med Biol. 2022 Aug 9;67(16):10.1088/1361-6560/ac838f. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac838f. Phys Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35868290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heart is a heavy burden: cardiac toxicity in radiation oncology.Support Care Cancer. 2024 Nov 4;32(11):769. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08949-7. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39495349 Review.
-
A Potential Pitfall and Clinical Solutions in Surface-Guided Deep Inspiration Breath Hold Radiation Therapy for Left-Sided Breast Cancer.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023 May 27;8(6):101276. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101276. eCollection 2023 Nov-Dec. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38047221 Free PMC article.
-
Explicitly encoding the cyclic nature of breathing signal allows for accurate breathing motion prediction in radiotherapy with minimal training data.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024 May 27;30:100594. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2024.100594. eCollection 2024 Apr. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38883146 Free PMC article.
-
Current Cardioprotective Strategies for the Prevention of Radiation-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Left-Sided Breast Cancer Patients.J Pers Med. 2023 Jun 24;13(7):1038. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071038. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37511651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of setup accuracy of optical surface image versus orthogonal x-ray images for VMAT of the left breast using deep-inspiration breath-hold.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Dec;24(12):e14117. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14117. Epub 2023 Aug 3. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 37535396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:987‐998. - PubMed
-
- Hjelstuen MH, Mjaaland I, Vikstrom J, et al. Radiation during deep inspiration allows loco‐regional treatment of left breast and axillary‐, supraclavicular‐ and internal mammary lymph nodes without compromising target coverage or dose restrictions to organs at risk. Acta Oncol. 2012;51:333‐344. - PubMed
-
- Vuong W, Garg R, Bourgeois DJ, et al. Dosimetric comparison of deep‐inspiration breath‐hold and free‐breathing treatment delivery techniques for left‐sided breast cancer using 3d surface tracking. Med Dosim. 2019;44:193‐198. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

