Patent landscape of inhibitors and PROTACs of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins
- PMID: 35993382
- PMCID: PMC9942934
- DOI: 10.1080/13543776.2022.2116311
Patent landscape of inhibitors and PROTACs of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins
Abstract
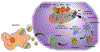
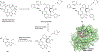
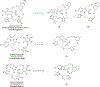
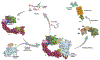
Introduction: The anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins, such as BCL-2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1, are excellent cancer therapeutic targets. The FDA approval of BCL-2 selective inhibitor venetoclax in 2016 validated the strategy of targeting these proteins with BH3 mimetic small molecule inhibitors.
Areas covered: This review provides an overview of the patent literature between 2016 and 2021 covering inhibitors and PROTACs of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins.
Expert opinion: Since the FDA approval of venetoclax, tremendous efforts have been made to develop its analogues with improved drug properties. These activities will likely result in new drugs in coming years. Significant progress on MCL-1 inhibitors has also been made, with multiple compounds entering clinical trials. However, MCL-1 inhibition could cause on-target toxicity to normal tissues especially the heart. Similar issue exists with BCL-XL inhibitors, which cause on-target platelet toxicity. To overcome this issue, several strategies have been applied, including prodrug, dendrimer-based drug delivery, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), and proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC); and amazingly, each of these approaches has resulted in a drug candidate entering clinical trials. We envision technologies like ADC and PROTAC could also be utilized to increase the therapeutic index of MCL-1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Apoptosis; BCL-2 protein family; BH3 mimetics; PROTACs; cancer therapy; protein–protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest
P Pal, P Zhang, and G Zheng disclose inventorship of reviewed BCL-XL/BCL-2 PROTAC filings. G Zheng is a co-founder and shareholder of Dialectic Therapeutics. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
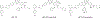
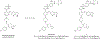

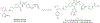

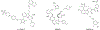
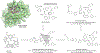
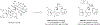
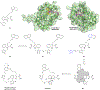


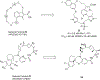
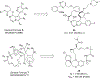
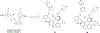
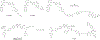
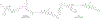
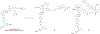
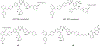
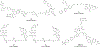
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
