Is there any additional benefit of 68Ga-PSMA PET on radiotherapy target volume definition in patients with glioblastoma?
- PMID: 35993417
- PMCID: PMC9793479
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20220049
Is there any additional benefit of 68Ga-PSMA PET on radiotherapy target volume definition in patients with glioblastoma?
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the contribution of 68Gallium (68Ga)-PSMA (prostate-specific membrane antigen) positron emission tomography (PET) in defining radiotherapy (RT) target volume for glioblastoma and to compare the target volumes defined by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
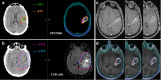
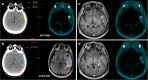
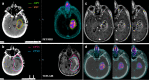
Methods: RT planning Computed Tomography (CT) images were fused separately with pre-operative MRI and PET/MRI images of 10 glioblastoma patients, retrospectively. The contrast-enhanced area in T1 weighted MRI was contoured as gross tumor volume (GTV) and clinical target volume (CTV1) was obtained by including the cavity and T2/FLAIR hyperintense areas after giving a margin of 2 cm to the GTV. 68Ga-PSMA uptake area was contoured as biological tumor volume (BTV) and CTV2 was obtained with a margin of 2 cm to BTV. Planning target volumes (PTVs) were created with the 3 mm added to the CTVs. Conformity index (CI), dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and overlap volume (OV) were calculated by obtaining the intersection and union volumes. Volumetric comparison, similarity and overlap analyzes were performed statistically by Wilcoxon signed rank and One sample t-test.
Results: The median GTV was 21,96 cc (1,04 - 82,04) and BTV was 25,58 cc (2,43 - 99,47). BTV was on average 47% larger than GTV which was statistically significant (p = 0.03). For GTV-BTV, CTV1-CTV2 and PTV1-PTV2; mean values of CI were 0,56, 0,76 and 0,76; DSC were 0,70, 0,86 and 0,86; OV were 0,88, 0,94 and 0,94, respectively. There was no significant difference on size and spatial similarity between CTV1 and CTV2, PTV1 and PTV2.
Conclusion: Altough BTV was larger than GTV, this significance was lost while we gave the same CTV margin including the peripheral edema. It seems that it may help to improve defining non-enhancing tumor part and also recurrent tumor volume.
Advances in knowledge: Recent studies have focused on the role of 68Ga-PSMA PET in imaging of glial tumors. It has been observed that 68Ga-PSMA PET can clearly define the tumor borders and it can be beneficial in target volume delineation, especially in reirradiation of recurrent tumors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gross tumor volume delineation in primary prostate cancer on 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/MRI and 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI.Cancer Imaging. 2022 Jul 22;22(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40644-022-00475-1. Cancer Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35869521 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 68Ga-HBED-CC PSMA-PET/CT and multiparametric MRI for gross tumour volume detection in patients with primary prostate cancer based on slice by slice comparison with histopathology.Theranostics. 2017 Jan 1;7(1):228-237. doi: 10.7150/thno.16638. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28042330 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation on the role of integrated PET/MRI for target volume definition and radiotherapy planning in patients with high grade glioma.Radiother Oncol. 2014 Sep;112(3):425-9. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Radiother Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25308182
-
Radiotherapy of high-grade gliomas: current standards and new concepts, innovations in imaging and radiotherapy, and new therapeutic approaches.Chin J Cancer. 2014 Jan;33(1):16-24. doi: 10.5732/cjc.013.10217. Chin J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24384237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Positron emission tomography for radiation treatment planning.Strahlenther Onkol. 2005 Aug;181(8):483-99. doi: 10.1007/s00066-005-1422-7. Strahlenther Onkol. 2005. PMID: 16044216 Review.
Cited by
-
Preferred Imaging for Target Volume Delineation for Radiotherapy of Recurrent Glioblastoma: A Literature Review of the Available Evidence.J Pers Med. 2024 May 17;14(5):538. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050538. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of 5-aminolevulinic acid and MMP-14 targeted peptide probes in preclinical models of GBM.Theranostics. 2025 Feb 24;15(8):3517-3531. doi: 10.7150/thno.107210. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40093889 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear medicine imaging modalities to detect incidentalomas and their impact on patient management: a systematic review.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 25;150(7):368. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05891-3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39052066 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Recurrent Glioblastoma Target Contours via 11C-Methionine, 68Ga-Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Implications for Precision Radiotherapy Planning.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2024 Jun 4;9(9):101548. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2024.101548. eCollection 2024 Sep. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39188994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. . European organisation for research and treatment of cancer brain tumor and radiotherapy groups; national cancer institute of canada clinical trials group. radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 987–96. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJB, Janzer RC, et al. . Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 459–66. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

