Comparison of the performance of Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx Assay with Abbott RealTime HIV Assay for viral load monitoring using plasma and Dried Blood Spots collected in Kenya
- PMID: 35994447
- PMCID: PMC9394820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269838
Comparison of the performance of Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx Assay with Abbott RealTime HIV Assay for viral load monitoring using plasma and Dried Blood Spots collected in Kenya
Abstract
Introduction: HIV-1 viral Load (VL) testing is recommended for the monitoring of antiretroviral treatment. Dried Blood Spots (DBS) are an effective sample type in resource limited settings, where safe phlebotomy and reliable shipping are hard to guarantee. In HIV high burden countries, high throughput assays can improve access to testing services. The Hologic Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx Assay (Aptima Assay) is a high throughput assay that runs on the CE-IVD approved Panther platform. The objectives of this study were to assess the performance characteristics of Aptima for VL monitoring using plasma and venous DBS specimens and to determine the stability of HIV-1 RNA in DBS.
Materials and methods: This was a cross-sectional study of 2227 HIV infected adults visiting health facilities in Nairobi and Busia, Kenya. Each provided a venous blood sample; plasma was prepared from 1312 samples while paired DBS samples and plasma were prepared from the remaining 915 samples. The agreement between the Aptima assay and the Abbott RealTime HIV-1 Assay (Abbott RT) was analysed by comparing the HIV-1 VL in both assays at the medical decision point of 1000 copies/mL. To assess stability of HIV-1 RNA in DBS, VL in DBS spotted on day 0 were compared with that from the same DBS card after 21 days of storage at room temperature.
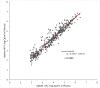
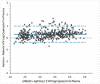
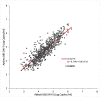
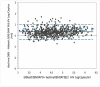
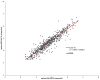
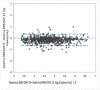
Results: Overall, 436 plasma samples had quantifiable results in both Aptima and Abbott RT. The agreement between the two assays at 1000 copies/mL was 97.48% with a Pearson's correlation coefficient (r) of 0.9589 and gave a mean bias of 0.33 log copies/mL on Bland-Altman analysis. For fresh DBS, the agreement in both assays was 94.64% at 1000 copies/mL, with an r of 0.8692 and a mean bias of 0.35 log copies/mL. The overall agreement between DBS tested in Aptima on day 0 versus day 21 was 95.71%, with a mean bias of -0.154.
Conclusion: The Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx assay is an accurate test for VL monitoring of HIV-1 using DBS and plasma sample types in Kenya.
Conflict of interest statement
Hologic, Inc. provided the funds and materials for the study. Sangeetha Nair and Sven Schaffer were employees of Hologic, Inc at the time of the study. The rest of the authors are employees of the Kenya Medical Research Institute and declare no conflict of interest. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective evaluation of accuracy of HIV viral load monitoring using the Aptima HIV Quant Dx assay with fingerstick and venous dried blood spots prepared under field conditions in Kenya.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 2;16(4):e0249376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249376. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33798221 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 viral load measurement in venous blood and fingerprick blood using Abbott RealTime HIV-1 DBS assay.J Clin Virol. 2017 Jul;92:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 13. J Clin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28531553
-
Performance evaluation of the Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx assay for detection of HIV in infants in Kenya.J Clin Virol. 2020 Apr;125:104289. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104289. Epub 2020 Feb 15. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32097889
-
Performances of Dried Blood Spots and Point-of-Care Devices to Identify Virological Failure in HIV-Infected Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2023 Feb;37(2):66-83. doi: 10.1089/apc.2022.0135. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2023. PMID: 36787410
-
Systematic review of the performance and clinical utility of point of care HIV-1 RNA testing for diagnosis and care.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 27;14(6):e0218369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218369. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31246963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS HIV and AIDS Statistics 2021 https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
-
- HIV/AIDS. 90-90-90: an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, Geneva, Switzerland. 2014.
-
- Rutherford GW, Anglemyer A, Easterbrook PJ, Horvath T, Vitoria M, Penazzato M, et al.. Predicting treatment failure in adults and children on antiretroviral therapy: a systematic review of the performance characteristics of the 2010 WHO immunologic and clinical criteria for virologic failure. AIDS. 2014;28 Suppl 2:S161–9. Epub 2014/05/23. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000236 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Organization WHO. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. 2016. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

