Contribution of keratinocytes to dermal fibrosis
- PMID: 35994728
- PMCID: PMC9594125
- DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000895
Contribution of keratinocytes to dermal fibrosis
Abstract
Purpose of review: The cellular pathogenesis of fibrotic disorders including systemic sclerosis (SSc) remains largely speculative. Currently, the altered function of endothelial cells and fibroblasts under the influence of an inappropriate immune response are considered central pathogenic events in SSc. Adding to this complexity, novel evidence here reviewed suggests that keratinocytes may concur in the development of skin fibrosis.
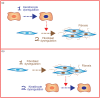
Recent findings: Epidermal equivalents (EE) generated from primary SSc keratinocytes display a distinct gene expression program when compared to healthy donor (HD) EE. SSc-EE, among others, exhibited enhanced oxidative and metabolic response pathways. Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated similarities between SSc-EE and SSc epidermis including altered keratinocyte differentiation, enhanced expression of activation markers, and reduced rate of basal keratinocytes proliferation. SSc-EE supernatants more than HD-EE modified the inflammatory and extracellular matrix deposition/resorption program of dermal fibroblasts. Further evidence indicated that the relative lack rather than the excess of interleukin-25 in keratinocytes may contribute to enhanced dermal fibrotic changes. Overall, these data support keratinocyte-intrinsic SSc-related modifications.
Summary: Improved methods for engineering epidermal and skin equivalents are helping to address the question whether keratinocyte alterations in SSc are primary and capable to dysregulate dermal homeostasis or secondary following dermal fibrotic changes.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Canady J, Arndt S, Karrer S, et al. . Increased KGF expression promotes fibroblast activation in a double paracrine manner resulting in cutaneous fibrosis. J Invest Dermatol 2013; 133:647–657. - PubMed
-
- Aden N, Nuttall A, Shiwen X, et al. . Epithelial cells promote fibroblast activation via IL-1alpha in systemic sclerosis. J Invest Dermatol 2010; 130:2191–2200. - PubMed
-
- Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Shiwen X, Denton CP, et al. . Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9. J Invest Dermatol 2014; 134:2693–2702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

