Clinical efficacy of sequential treatments in KRASG12C-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: findings from a real-life multicenter Italian study (CRC-KR GOIM)
- PMID: 35994791
- PMCID: PMC9588891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100567
Clinical efficacy of sequential treatments in KRASG12C-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: findings from a real-life multicenter Italian study (CRC-KR GOIM)
Abstract
Background: The presence of KRASG12C mutation in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) correlates with poor outcome. Although different selective inhibitors are under clinical development, the optimal treatment remains uncertain. Thus, we conducted a retrospective analysis in a large cohort of patients with KRASG12C mCRC treated in 12 Italian oncology units.
Patients and methods: Patients with unresectable mCRC harboring KRASG12C mutation receiving a first-line chemotherapy doublet or triplet between 2011 and 2021 were included in the study. Evaluation of overall response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) analysis was carried out.
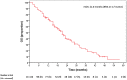
Results: A total of 256/6952 (3.7%) patients with mCRC displayed KRASG12C mutation; of these, 111 met the inclusion criteria. The ORR of first-line therapy was 38.7% (43/111). Median PFS (mPFS) was 9 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 7.5-10.5 months]. After progression, only 62% and 36% of the patients are fit to receive second or third lines of treatment, with limited clinical benefit. Median OS (mOS) was 21 months (95% CI 17.4-24.6 months). In patients receiving first-line triplet chemotherapy, ORR was 56.3% (9/16), mPFS was 13 months (95% CI 10.3-15.7 months) and mOS was 32 months (95% CI 7.7-56.3 months). For irinotecan-based doublets, ORR was 34.5 (10/29), mPFS was 9 months (95% CI 6.4-11.6 months) and mOS was 22 months (95% CI 16.0-28.0 months). With oxaliplatin-based doublets ORR was 36.4% (24/62), mPFS was 7 months (95% CI 4.6-9.4 months) and mOS was 18 months (95% CI, 13.6-22.4 months).
Conclusion: Patients with KRASG12C-mutant mCRC had a disappointing response to standard treatments. Within the limitations of a retrospective study, these results suggest that first-line chemotherapy intensification with FOLFOXIRI is a valid option in fit patients.
Keywords: KRASG12C mutation; chemotherapy; first line treatment; mCRC; real-world data.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ciardiello F., Ciardiello D., Martini G., Napolitano S., Tabernero J., Cervantes A. Clinical management of metastatic colorectal cancer in the era of precision medicine. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:372–401. - PubMed
-
- Martinelli E., Ciardiello D., Martini G., et al. Implementing anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: challenges and future perspectives. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(1):30–40. - PubMed
-
- André T., Shiu K.K., Kim T.W., et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(23):2207–2218. - PubMed
-
- Lenz H.J., Van Cutsem E., Luisa Limon M., et al. First-line nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab for microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase II CheckMate 142 study. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(2):161–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

