Immunogenicity to COVID-19 mRNA vaccine third dose in people living with HIV
- PMID: 35995780
- PMCID: PMC9395398
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32263-7
Immunogenicity to COVID-19 mRNA vaccine third dose in people living with HIV
Abstract
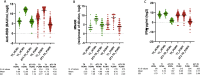
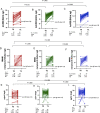
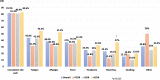
In order to investigate safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine third dose in people living with HIV (PLWH), we analyze anti-RBD, microneutralization assay and IFN-γ production in 216 PLWH on ART with advanced disease (CD4 count <200 cell/mm3 and/or previous AIDS) receiving the third dose of a mRNA vaccine (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273) after a median of 142 days from the second dose. Median age is 54 years, median CD4 nadir 45 cell/mm3 (20-122), 93% HIV-RNA < 50 c/mL. In 68% of PLWH at least one side-effect, generally mild, is recorded. Humoral response after the third dose was strong and higher than that achieved with the second dose (>2 log2 difference), especially when a heterologous combination with mRNA-1273 as third shot is used. In contrast, cell-mediated immunity remain stable. Our data support usefulness of third dose in PLWH currently receiving suppressive ART who presented with severe immune dysregulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID19) Dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- Nasreen, S. et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against variants of concern in Ontario, Canada. medRxiv. 06.28.21259420; 10.1101/2021.06.28.21259420. (2021)
-
- Comirnaty and Spikevax: EMA recommendations on extra doses and boosters. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/comirnaty-spikevax-ema-recommendations....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

