Honghua extract mediated potent inhibition of COVID-19 host cell pathways
- PMID: 35995784
- PMCID: PMC9395372
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15338-9
Honghua extract mediated potent inhibition of COVID-19 host cell pathways
Abstract
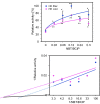
Honghua (Carthami flos) and Xihonghua (Croci stigma) have been used in anti-COVID-19 as Traditional Chinese Medicine, but the mechanism is unclear. In this study, we applied network pharmacology by analysis of active compounds and compound-targets networks, enzyme kinetics assay, signaling pathway analysis and investigated the potential mechanisms of anti-COVID-19. We found that both herbs act on signaling including kinases, response to inflammation and virus. Moreover, crocin likely has an antiviral effect due to its high affinity towards the human ACE2 receptor by simulation. The extract of Honghua and Xihonghua exhibited nanozyme/herbzyme activity of alkaline phosphatase, with distinct fluorescence. Thus, our data suggest the great potential of Honghua in the development of anti-COVID-19 agents.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Data mining analysis of regularity of formulas containing Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma-Carthami Flos medicin pair in Dictionary of Chinese Medicine Prescription].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;41(3):528-531. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20160328. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28868875 Chinese.
-
Potential effect of Maxing Shigan decoction against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) revealed by network pharmacology and experimental verification.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 May 10;271:113854. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113854. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33513419 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology, molecular docking integrated surface plasmon resonance technology reveals the mechanism of Toujie Quwen Granules against coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia.Phytomedicine. 2021 May;85:153401. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153401. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33191068 Free PMC article.
-
[Research of Chinese medicine pairs (VIII)--Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma-Carthami flos].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Dec;38(24):4227-31. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24791521 Review. Chinese.
-
The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 21;102(16):e33593. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033593. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37083803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance and immune infiltration analysis of HMGA2 in endometrial cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 9;16:1559278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1559278. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40703517 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of Zhenzhu Pills treating intracerebral hemorrhage secondary injury based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 16;103(7):e36837. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036837. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38363944 Free PMC article.
-
Wogonin inhibits the proliferation of prolactinoma through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 15;16:1546285. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1546285. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40444042 Free PMC article.
-
Potential herb‒drug interactions between anti-COVID-19 drugs and traditional Chinese medicine.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Jun 5;13(9):3598-637. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.001. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37360014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in herbal medicine-based nanozymes for biomedical applications.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 May 5;138(9):1037-1049. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003584. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40169370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benassi E, Fan H, Sun Q, Dukenbayev K, Wang Q, Shaimoldina A, Tassanbiyeva A, Nurtay L, Nurkesh A, Kutzhanova A, Mu C, Dautov A, Razbekova M, Kabylda A, Yang Q, Li Z, Amin A, Li X, Xie Y. Generation of particle assemblies mimicking enzymatic activity by processing of herbal food: The case of rhizoma polygonati and other natural ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine. Nanoscale Adv. 2021;3:2222–2235. doi: 10.1039/D0NA00958J. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tu Y, Xue Y, Guo D, Sun L, Guo M. Carthami flos: A review of its ethnopharmacology, pharmacology and clinical applications. Rev. Bras. 2015;25(5):553–566.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

