Neutralization titer biomarker for antibody-mediated prevention of HIV-1 acquisition
- PMID: 35995954
- PMCID: PMC9499869
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01953-6
Neutralization titer biomarker for antibody-mediated prevention of HIV-1 acquisition
Abstract
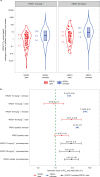
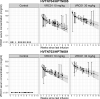
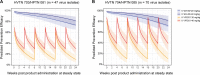
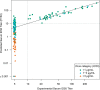
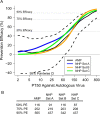
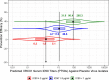
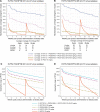
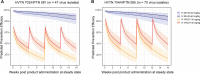
The Antibody Mediated Prevention trials showed that the broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb) VRC01 prevented acquisition of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) sensitive to VRC01. Using AMP trial data, here we show that the predicted serum neutralization 80% inhibitory dilution titer (PT80) biomarker-which quantifies the neutralization potency of antibodies in an individual's serum against an HIV-1 isolate-can be used to predict HIV-1 prevention efficacy. Similar to the results of nonhuman primate studies, an average PT80 of 200 (meaning a bnAb concentration 200-fold higher than that required to reduce infection by 80% in vitro) against a population of probable exposing viruses was estimated to be required for 90% prevention efficacy against acquisition of these viruses. Based on this result, we suggest that the goal of sustained PT80 <200 against 90% of circulating viruses can be achieved by promising bnAb regimens engineered for long half-lives. We propose the PT80 biomarker as a surrogate endpoint for evaluatinon of bnAb regimens, and as a tool for benchmarking candidate bnAb-inducing vaccines.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K25 AI155224/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068614/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068618/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131251/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI064518/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI054165/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI152115/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

