Diagnosis of paediatric TB using Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra on fresh respiratory samples
- PMID: 35996291
- PMCID: PMC9423021
- DOI: 10.5588/ijtld.22.0007
Diagnosis of paediatric TB using Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra on fresh respiratory samples
Abstract
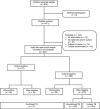
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra (Ultra) on fresh respiratory samples for the diagnosis of pulmonary TB (PTB) in children.METHODS: Between July 2017 and December 2019, children with presumed TB were prospectively enrolled at clinical sites in three African countries. Children were assessed using history, physical examination and chest X-ray. Sputum or gastric aspirate samples were analysed using Ultra and culture. The diagnostic accuracy of Ultra was calculated against culture as the reference standard.RESULTS: In total, 547children were included. The median age was 4.7 years, 77 (14.1%) were HIV infected and 77 (14.1%) had bacteriologically confirmed TB. Ultra detected an additional 20 cases in the group of children with negative culture results. The sensitivity of Ultra was 66.3% (95% CI 47-82), and the specificity was 95.4% (95% CI 89-99) when assessed against culture as the reference standard.CONCLUSION: Despite the improved performance of Ultra as compared to Xpert as was previously reported, its sensitivity remains sub-optimal for the detection of TB in children. Ultra detected additional 20 cases which otherwise could not have been detected by culture alone, suggesting that the latter is an imperfect reference standard.
OBJECTIF :: Évaluer la précision diagnostique de Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra (Ultra) sur des échantillons respiratoires frais pour le diagnostic de la TB pulmonaire (PTB) chez les enfants.
MÉTHODES :: Entre juillet 2017 et décembre 2019, des enfants présentant une TB présumée ont été inscrits de manière prospective dans des sites cliniques de trois pays africains. Les enfants ont été évalués à l’aide d’antécédents, d’un examen physique et d’une radiographie pulmonaire. Les échantillons d’expectoration ou d’aspiration gastrique ont été analysés à l’aide de l’Ultra et de la culture. La précision diagnostique de l’Ultra a été calculée par rapport à la culture comme norme de référence.
RÉSULTATS :: Au total, 547 enfants ont été inclus. L’âge médian était de 4,7 ans, 77 (14,1%) étaient infectés par le VIH et 77 (14,1%) avaient une TB confirmée bactériologiquement. L’Ultra a détecté 20 cas supplémentaires dans le groupe d’enfants dont les résultats de culture étaient négatifs. La sensibilité de l’Ultra était de 66,3% (IC 95% 47–82) et la spécificité de 95,4% (IC 95% 89–99) par rapport à la culture comme norme de référence.
CONCLUSION :: Malgré l’amélioration des performances de l’Ultra par rapport à l’Xpert, comme cela a été précédemment rapporté, sa sensibilité reste sous-optimale pour la détection de la TB chez les enfants. Ultra a détecté 20 cas supplémentaires qui n’auraient pas pu être détectés par la culture seule, ce qui suggère que cette dernière est un standard de référence imparfait.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none declared.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2021. Global tuberculosis report, 2021.
-
- World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2014. Xpert MTB/RIF: WHO policy update and implementation manual.
-
- Rachow A, et al. Increased and expedited case detection by Xpert MTB/RIF assay in childhood tuberculosis: a prospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(10):1388–1396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

