Mobile human ad hoc networks: A communication engineering viewpoint on interhuman airborne pathogen transmission
- PMID: 35996611
- PMCID: PMC9385271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nancom.2022.100410
Mobile human ad hoc networks: A communication engineering viewpoint on interhuman airborne pathogen transmission
Abstract
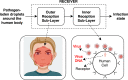
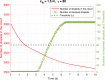
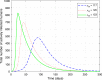
A number of transmission models for airborne pathogens transmission, as required to understand airborne infectious diseases such as COVID-19, have been proposed independently from each other, at different scales, and by researchers from various disciplines. We propose a communication engineering approach that blends different disciplines such as epidemiology, biology, medicine, and fluid dynamics. The aim is to present a unified framework using communication engineering, and to highlight future research directions for modeling the spread of infectious diseases through airborne transmission. We introduce the concept of mobile human ad hoc networks (MoHANETs), which exploits the similarity of airborne transmission-driven human groups with mobile ad hoc networks and uses molecular communication as the enabling paradigm. In the MoHANET architecture, a layered structure is employed where the infectious human emitting pathogen-laden droplets and the exposed human to these droplets are considered as the transmitter and receiver, respectively. Our proof-of-concept results, which we validated using empirical COVID-19 data, clearly demonstrate the ability of our MoHANET architecture to predict the dynamics of infectious diseases by considering the propagation of pathogen-laden droplets, their reception and mobility of humans.
Keywords: Airborne pathogen transmission; COVID-19; Epidemiology; Infectious disease; Mobile human ad hoc networks; Molecular communication.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Brauer F., Castillo-Chavez C., Feng Z. Springer; 2019. Mathematical Models in Epidemiology, vol. 32.
-
- Bourouiba L. The fluid dynamics of disease transmission. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2021;53:473–508.
-
- Mittal R., Ni R., Seo J.-H. The flow physics of COVID-19. J. Fluid Mech. 2020;894
-
- Khalid M., et al. Communication through breath: Aerosol transmission. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019;57(2):33–39.
-
- Khalid M., Amin O., Ahmed S., Shihada B., Alouini M.-S. Modeling of viral aerosol transmission and detection. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020;68(8):4859–4873.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
