Levels of Pathogenic Th17 and Th22 Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 35996623
- PMCID: PMC9392632
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5398743
Levels of Pathogenic Th17 and Th22 Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
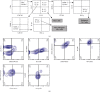
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized, among others, by tissue damage and activation/differentiation of proinflammatory lymphocytes. Accordingly, several studies have concluded that type 17 T helper (Th17) cells seem to have an important role in the pathogenesis of this condition. However, the strategy for the identification and analysis of proinflammatory Th17 cells in those studies has not been consistent and has usually been different from what was originally described. Therefore, we decided to evaluate the levels of Th17 cells in patients with RA employing an extended immune phenotype by using an eight-color multiparametric flow cytometry analysis. For this purpose, blood samples were obtained from 30 patients with RA and 16 healthy subjects, and the levels of Th17 and type 22 helper (Th22) lymphocytes were analyzed as well as the in vitro differentiation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells into Th17 lymphocytes induced by interleukin-23 (IL-23) and IL-1β. We found significant enhanced levels of total Th17 lymphocytes (defined as CD4+IL-17+) as well as enhanced numbers of their pathogenic (defined as CD4+CXCR3+IL-17+IL-22+CD243+CD161+IFN-γ +IL-10-) and nonpathogenic (CD4+CXCR3+IL-17+IL-22-CD243-CD161-IFN-γ -IL-10+) cell subsets in patients with RA. Likewise, the number of Th22 (CD4+CXCR3+/-IL-17-IL-22+) was also increased in these patients compared to healthy controls. However, the in vitro induction/differentiation of pathogenic Th17 cells showed similar results in controls and patients with RA. Likewise, no significant associations were detected in patients with RA between the levels of Th17 or Th22 cells and clinical or laboratory parameters. Our data indicate that patients with RA show enhanced blood levels of the different subsets of Th17 cells and Th22 lymphocytes tested in this study and suggest that these levels are not apparently associated with clinical or laboratory parameters.
Copyright © 2022 Marlen Vitales-Noyola et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MV-N, BH-C, DA-H, LB, SB-S, CA-M, PN-M, and RG-A have nothing to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elevated Th22 cells correlated with Th17 cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Immunol. 2011 Aug;31(4):606-14. doi: 10.1007/s10875-011-9540-8. Epub 2011 May 10. J Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21556937
-
Increased frequencies of Th22 cells as well as Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e31000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031000. Epub 2012 Apr 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22485125 Free PMC article.
-
Imbalance of Th17, Treg, and helper innate lymphoid cell in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;41(12):3837-3849. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06315-8. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35925523 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of Peripheral Th17 Cells and Th17-Related Cytokines in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Meta-analysis.Adv Ther. 2022 Oct;39(10):4423-4439. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02240-z. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35960483 Review.
-
IL-22 as a target for therapeutic intervention: Current knowledge on its role in various diseases.Cytokine. 2023 Sep;169:156293. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156293. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Cytokine. 2023. PMID: 37441942 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2024 May 25;13(11):915. doi: 10.3390/cells13110915. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria: a breakthrough in combating rheumatoid arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 5;11:1439182. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1439182. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39161412 Free PMC article.
-
Id2 exacerbates the development of rheumatoid arthritis by increasing IFN-γ production in CD4+ T cells.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70242. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70242. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40051059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen D. Y., Chen Y. M., Chen H. H., Hsieh C. W., Lin C. C., Lan J. L. Increasing levels of circulating Th17 cells and interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-α therapy. Arthritis Research & Therapy . 2011;13(4):p. R126. doi: 10.1186/ar3431. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McGovern J. L., Nguyen D. X., Notley C. A., Mauri C., Isenberg D. A., Ehrenstein M. R. Th17 cells are restrained by Treg cells via the inhibition of interleukin-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis responding to anti–tumor necrosis factor antibody therapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism . 2012;64(10):3129–3138. doi: 10.1002/art.34565. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

