Cardiovascular biomarkers in body fluids: progress and prospects in optical sensors
- PMID: 35996626
- PMCID: PMC9386656
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-022-00990-2
Cardiovascular biomarkers in body fluids: progress and prospects in optical sensors
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the major causative factors for high mortality and morbidity in developing and developed nations. The biomarker detection plays a crucial role in the early diagnosis of several non-infectious and life-threatening diseases like CVD and many cancers, which in turn will help in more successful therapy, reducing the mortality rate. Biomarkers have diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic significances. The search for novel biomarkers using proteomics, bio-sensing, micro-fluidics, and spectroscopic techniques with good sensitivity and specificity for CVD is progressing rapidly at present, in addition to the use of gold standard biomarkers like troponin. This review is dealing with the current progress and prospects in biomarker research for the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Expert opinion. Fast diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) can help to provide rapid medical intervention, which can affect the patient's short and long-term health. Identification and detection of proper biomarkers for early diagnosis are crucial for successful therapy and prognosis of CVDs. The present review discusses the analysis of clinical samples such as whole blood, blood serum, and other body fluids using techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography-LASER/LED-induced fluorescence, Raman spectroscopy, mainly, optical methods, combined with nanotechnology and micro-fluidic technologies, to probe patterns of multiple markers (marker signatures) as compared to conventional techniques.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cardiovascular Diseases; Omics methods; Spectroscopy techniques.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
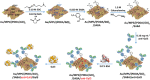
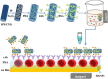
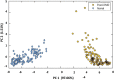
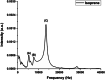
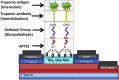


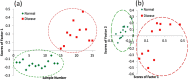
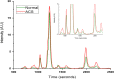
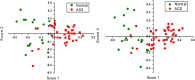
References
-
- A berezin E 2018 Circulating biomarkers in heart failure From Research to Clinical Practice 89–108 10.1007/5584
-
- Addisu, Shimeles, Terefe Tafese, Chen Xu, Muhammad Saqib, Haijuan Li, and Yongdong Jin. 2021. “Plasmon-enhanced quantum dots electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for selective and sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I.” Talanta 221 (September 2020): 121674. 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121674 - PubMed
-
- Adzhri AMK, Arshad SCB, Gopinath R, Ruslinda MFM, Fathil CI, Nuzaihan MN. Enhanced sensitivity mediated ambipolar conduction with P-type TiO2 anatase transducer for biomarker capturing. Sens Actuators, A. 2017;259:57–67. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2017.03.015. - DOI
-
- Alaaraji Shakir F T. Is there a correlation between monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with autotaxin, azurocidin-1, apolipoprotein C-III and elastase-2 in male Iraqi acute myocardial infraction patients ? Biomedical & Pharmacology Journal. 2019;12(4):2105–21. doi: 10.13005/bpj/1846. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

