Prevalence of acute kidney injury amongst Covid-19 admitted patients in Ribat Teaching Hospital isolation centre: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- PMID: 35996634
- PMCID: PMC9387061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104404
Prevalence of acute kidney injury amongst Covid-19 admitted patients in Ribat Teaching Hospital isolation centre: A retrospective cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Covid-19 sequeale have been a cause of serious health concerns since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic. Studies regarding this are still lacking especially in relation to the prevalence of Covid-19 induced AKI. Therefore, we have aimed to determine the prevalence of AKI amongst Covid-19 hospitalised patients in Ribat isolation centre.
Methodology: A cross-sectional retrospective study was conducted in the period from March 2020 to July 2021 in Ribat teaching hospital primary isolation centre which includes admitted Covid-19 induced AKI patients. A total of 333 confirmed Covid-19 patients were tested out of which we analyzed 183 files that fit the criteria of our research. The data was collected from the patients' record files using a checklist.
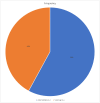
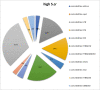
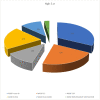
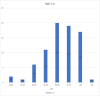
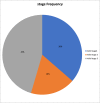
Results: A total of 77 out of 183 patients (42%) of admitted patients were diagnosed with AKI, out of which 35 patients had stage 3 AKI (46%), followed by 28 (36%) and 14 (18%) regarding stage 1 and stage 2 respectively. Furthermore, 57 out of the total 77 (74%) aged 60 years and above.
Conclusion: This study substantiates the theory that Covid-19 induces AKI regardless of its severity and the presence of co-morbidities. Additionally, older age (60 years and above) was the most important risk factor associated with it. Furthermore, most cases of Covid-19 induced AKI were stage 3.
Keywords: AKI; Covid-19.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All author report no conflict of interest of any kind.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential Association of Hypernatremia With Mortality in Patients With Acute Kidney Injury and COVID-19.Cureus. 2022 Jul 31;14(7):e27530. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27530. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36060411 Free PMC article.
-
Are we aware of COVID-19-related acute kidney injury in intensive care units?Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Mar;26(5):1753-1760. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202203_28245. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35302225
-
Chronic anticoagulation is not associated with a reduced risk of acute kidney injury in hospitalised Covid-19 patients.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Jun 16;22(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02436-5. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34134645 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Use of Dialysis Associated With an Increased Risk of Death in COVID-19-Related Acute Kidney Injury?Cureus. 2022 Dec 10;14(12):e32373. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32373. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36632264 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Complications of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Res Health Sci. 2021 Jan 12;21(1):e00503. doi: 10.34172/jrhs.2021.39. J Res Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 34024761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Hougenhouck-Tulleken, Hussain, do Vale. 2021. Acute Kidney Injury in Covid-19 Infection: what Are the Outcomes in South Africa. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

