Comparison of Outcomes of Multi-Level Anterior, Oblique, Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery : Impact on Global Sagittal Alignment
- PMID: 35996945
- PMCID: PMC9837492
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2022.0112
Comparison of Outcomes of Multi-Level Anterior, Oblique, Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery : Impact on Global Sagittal Alignment
Abstract
Objective: To compare the outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF), oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF), and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) in terms of global sagittal alignment.
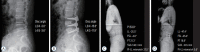
Methods: From January 2007 to December 2019, 141 adult patients who underwent multilevel interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative disorders were enrolled. Regarding the approach, patients were divided into the ALIF (n=23), OLIF (n=60), and TLIF (n=58) groups. Outcomes, including local radiographic parameters and global sagittal alignment, were then compared between the treatment groups.
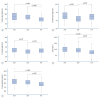
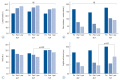
Results: Regarding local radiographic parameters, ALIF and OLIF were superior to TLIF in terms of the change in the anterior disc height (7.6±4.5 mm vs. 6.9±3.2 mm vs. 4.7±2.9 mm, p<0.001), disc angle (-10.0°±6.3° vs. -9.2°±5.2° vs. -5.1°±5.1°, p<0.001), and fused segment lordosis (-14.5°±11.3° vs. -13.8°±7.5° vs. -7.4°±9.1°, p<0.001). However, regarding global sagittal alignment, postoperative lumbar lordosis (-42.5°±9.6° vs. -44.4°±11.6° vs. -40.6°±12.3°, p=0.210), pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch (7.9°±11.3° vs. 6.7°±11.6° vs. 11.5°±13.0°, p=0.089), and the sagittal vertical axis (24.3±28.5 mm vs. 24.5±34.0 mm vs. 25.2±36.6 mm, p=0.990) did not differ between the groups.
Conclusion: Although the anterior approaches were superior in terms of local radiographic parameters, TLIF achieved adequate global sagittal alignment, comparable to the anterior approaches.
Keywords: Anterior lumbar interbody fusion; Lordosis; Lumbar vertebrae; Oblique lumbar interbody fusion; Spinal fusion; Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Does approach matter? A comparative radiographic analysis of spinopelvic parameters in single-level lumbar fusion.Spine J. 2018 Nov;18(11):1999-2008. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29631061
-
[Effects of oblique lateral interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lordosis correction in degenerative lumbar diseases].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jul 3;98(25):1990-1995. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.25.005. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29996598 Chinese.
-
Technical Consideration for TLIF Cage Retrieval and Deformity Correction With Anterior Interbody Fusion in Lumbar Revision Surgeries.Spine Deform. 2019 Jul;7(4):633-640. doi: 10.1016/j.jspd.2018.10.004. Spine Deform. 2019. PMID: 31202382
-
Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus oblique lateral interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative disease: a meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Sep 18;22(1):802. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04687-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34537023 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of lumbar lordosis after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review.Spine J. 2019 May;19(5):951-958. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.10.017. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30529420
Cited by
-
Fusion rate and complications of oblique lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis.Front Surg. 2024 Apr 30;11:1374134. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1374134. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38746621 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Injury Incidence and Radiological Outcomes in OLIF L5/S1: Iliac Bifurcation Versus Prepsoas Approach.Korean J Neurotrauma. 2025 Jul 22;21(3):183-192. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2025.21.e24. eCollection 2025 Jul. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2025. PMID: 40778255 Free PMC article.
-
The Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Narrative Review, and Future Perspective.Neurospine. 2023 Dec;20(4):1224-1245. doi: 10.14245/ns.2346888.444. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Neurospine. 2023. PMID: 38171291 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oblique lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Sep;143(9):5657-5670. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-04880-4. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 37079105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chung HW, Lee HD, Jeon CH, Chung NS. Comparison of surgical outcomes between oblique lateral interbody fusion (OLIF) and anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021;209:106901. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O’Shaughnessy BA, Sugrue P, Salehi S, Ondra S, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7:379–386. - PubMed
-
- Hyun SJ, Yoon SH, Kim JH, Oh JK, Lee CH, Shin JJ, et al. A prospective, multi-center, double-blind, randomized study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the synthetic bone graft material DBM gel with rhBMP-2 versus DBM gel used during the TLIF procedure in patients with lumbar disc disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021;64:562–574. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

