Angiogenic Potential of Co-Cultured Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells and Adipose Stromal Cells in Customizable 3D Engineered Collagen Sheets
- PMID: 35997445
- PMCID: PMC9397038
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb13030107
Angiogenic Potential of Co-Cultured Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells and Adipose Stromal Cells in Customizable 3D Engineered Collagen Sheets
Abstract
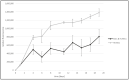
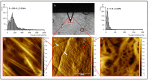
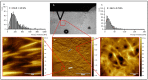
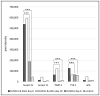
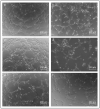
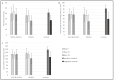
The wound healing process is much more complex than just the four phases of hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. Three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds made of biopolymers or ECM molecules using bioprinting can be used to promote the wound healing process, especially for complex 3D tissue lesions like chronic wounds. Here, a 3D-printed mold has been designed to produce customizable collagen type-I sheets containing human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and adipose stromal cells (ASCs) for the first time. In these 3D collagen sheets, the cellular activity leads to a restructuring of the collagen matrix. The upregulation of the growth factors Serpin E1 and TIMP-1 could be demonstrated in the 3D scaffolds with ACSs and HUVECs in co-culture. Both growth factors play a key role in the wound healing process. The capillary-like tube formation of HUVECs treated with supernatant from the collagen sheets revealed the secretion of angiogenic growth factors. Altogether, this demonstrates that collagen type I combined with the co-cultivation of HUVECs and ACSs has the potential to accelerate the process of angiogenesis and, thereby, might promote wound healing.
Keywords: 3D biomimetic scaffolds; 3D collagen sheet; adipose stromal cells (ASCs); biomaterials; cell–biomaterial interface; human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs); regenerative medicine; tissue engineering; tissues and organs; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Schultz G., Chin G., Moldawer L., Diegelmann R. Ch23 Mechanisms of Vascular Disease. University of Adelaide Press; Adelaide, Australia: 2011.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

