Acute Q Fever with Atrioventricular Block, Israel
- PMID: 35997621
- PMCID: PMC9423905
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2809.212565
Acute Q Fever with Atrioventricular Block, Israel
Abstract
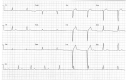
Cardiac involvement in acute Q fever is rare. We report 2 cases of an advanced atrioventricular block in young adult patients in Israel who sought care for acute Q fever without evidence of myocarditis. Q fever should be suspected in unexplained conduction abnormalities, especially in febrile young patients residing in disease-endemic areas.
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii; Israel; Q fever; atrioventricular block; bacteria; zoonoses.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson A, Bijlmer H, Fournier P-E, Graves S, Hartzell J, Kersh GJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of Q fever—United States, 2013: recommendations from CDC and the Q Fever Working Group. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013;62(RR-03):1–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

