Content and stability of B complex vitamins in commercial cosmetic products
- PMID: 35997631
- PMCID: PMC10087468
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.15321
Content and stability of B complex vitamins in commercial cosmetic products
Abstract
Background: Individual B vitamins have many favorable effects on the skin and are common cosmetic ingredients. However, their formulation is demanding due to stability issues, which consequently affect the products' quality.
Aims: We aimed to determine the quality (labeling accuracy, content determination, and content-related quality control) and stability under long-term and accelerated storage conditions of a representative sample of commercial cosmetics containing the most common B vitamins - nicotinamide, dexpanthenol, pyridoxine, and cyanocobalamin.
Methods: Cyanocobalamin was determined by a previously published stability-indicating HPLC- diode array detector (DAD) method for the simultaneous determination of all hydrophilic vitamins. This method was additionally simplified and adjusted for the time-effective analysis of nicotinamide, dexpanthenol, and pyridoxine. Both methods were properly validated.
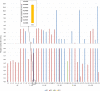
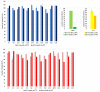
Results: All labeled B vitamins were present in the 36 tested products, mostly in contents, reported effective on the skin. Thus, a straightforward correlation between vitamin contents and product prices were not observed. The content-related quality control of eight products, which quantitively specify their content, revealed significantly lower nicotinamide contents (47% and 57%) in two products and appropriate or higher nicotinamide (102%-112%) and dexpanthenol (100%-104%) contents than declared in the remaining products. The 6-month long-term and accelerated stability studies demonstrated the products' physical stability, but also revealed dexpanthenol, pyridoxine, and cyanocobalamin degradation, while nicotinamide was mostly stable in the tested products.
Conclusions: The obtained results provide an inside into the quality of commercial vitamin B cosmetics and highlight the importance of stability testing in the formulation of quality, efficient, and safe cosmetics.
Keywords: D-panthenol; cosmeceuticals; cosmetic formulation; niacinamide (nicotinamide); stability; vitamin B3.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Simultaneous HPLC determination of thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin, nicotinamide and calcium folinate in multivitamin preparations].Boll Chim Farm. 1983 Apr;122(4):205-8. Boll Chim Farm. 1983. PMID: 6225447 Italian. No abstract available.
-
[INTERVENTION OF HYDROSOLUBLE VITAMINS OF THE B COMPLEX IN OSSIFICATION PROCESSES].Gazz Int Med Chir. 1964 Sep 15;68:1639-44. Gazz Int Med Chir. 1964. PMID: 14192000 Italian. No abstract available.
-
Simultaneous determination of some water-soluble vitamins and preservatives in multivitamin syrup by validated stability-indicating high-performance liquid chromatography method.J Chromatogr A. 2008 Aug 22;1202(2):155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.06.039. Epub 2008 Jul 3. J Chromatogr A. 2008. PMID: 18644604
-
[THE VITAMIN CONTROL OF STEROL AND STEROID METABOLISM].Ann Nutr Aliment. 1964;18:C357-87. Ann Nutr Aliment. 1964. PMID: 14238543 Review. French. No abstract available.
-
[Nipiopharmacology of vitamins].Minerva Nipiol. 1967 Nov-Dec;17(6):325-63. Minerva Nipiol. 1967. PMID: 4240934 Review. Italian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Folic Acid-Intercalated Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxides-A Multifunctional Nanohybrid Delivery System for Topical Applications.ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 26;9(49):48185-48195. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05374. eCollection 2024 Dec 10. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39676977 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Analytical Approach for Quality Control of Collagen in Food Supplements.Mar Drugs. 2024 Sep 26;22(10):435. doi: 10.3390/md22100435. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39452843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wargala E, Sławska M, Zalewska A, Toporowska M. Health effects of dyes, minerals, and vitamins used in cosmetics. Women. 2021;1(4):223‐237. doi:10.3390/women1040020 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

