The role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: an analysis of the treatment patterns, survival and toxicity rates by sex
- PMID: 35997822
- PMCID: PMC10314838
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04309-2
The role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: an analysis of the treatment patterns, survival and toxicity rates by sex
Abstract
Purpose: Our aim is to describe the role of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in clinical practice by providing the patient and tumor characteristics as well as survival and toxicity rates by sex.
Methods: We used electronic health records to identify patients treated at the Cancer Center of the University Hospital Bern, Switzerland between January 1, 2017 and June 16, 2021.
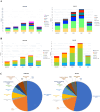
Results: We identified 5109 patients, 689 of whom (13.5%) received at least one dose of ICI. The fraction of patients who were prescribed ICI increased from 8.6% in 2017 to 22.9% in 2021. ICI represented 13.2% of the anticancer treatments in 2017 and increased to 28.2% in 2021. The majority of patients were male (68.7%), who were older than the female patients (median age 67 vs. 61 years). Over time, adjuvant and first line treatments increased for both sexes. Lung cancer and melanoma were the most common cancer types in males and females. The incidence of irAEs was higher among females (38.4% vs. 28.1%) and lead more often to treatment discontination in females than in males (21.1% vs. 16.8%). Independent of sex, the occurrence of irAEs was associated with greater median overall survival (OS, not reached vs. 1.1 years). Female patients had a longer median OS than males (1.9 vs. 1.5 years).
Conclusions: ICI play an increasingly important role in oncology. irAEs are more frequent in female patients and are associated with a longer OS. More research is needed to understand the association between patient sex and toxicity and survival.
Keywords: Age; Clinical practice; Gender; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Real-world; Role; Sex.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
BCÖ declared receiving institutional honoraria for lectures and advisory boards from BMS, MSD, Merck, Ipsen, Roche, Pfizer, Novartis. SHäfliger declared receiving honoraria for advisory boards from Bayer AstraZeneca Lilly Novartis Roche Takeda; and travel fee from Amgen. All the other authors declared to have no conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Beaver JA, Pazdur R (2021) The wild west of checkpoint inhibitor development. N Engl J Med. 10.1056/NEJMp2116863 - PubMed
-
- Byrne MM, Tannenbaum SL, Gluck S, Hurley J, Antoni M (2014) Participation in cancer clinical trials: why are patients not participating? Med Decis Making 34:116–126 - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Nie J, Dai L, Hu W, Zhang J, Han J, Ma X, Tian G, Han S, Wu D, Wang Y, Long J, Zhang Z, Fang J (2021) Immune-related adverse events and their association with the effectiveness of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: a real-world study from China. Front Oncol 11:607531 - PMC - PubMed
-
- CM Cramer-van der Welle, MV Verschueren, M Tonn, BJM Peters, Fmnh Schramel, OH Klungel, HJM Groen, EMW van de Garde, Nsclc Study Group Santeon (2021) Real-world outcomes versus clinical trial results of immunotherapy in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in the Netherlands. Sci Rep 11:6306 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

