Mobile phone addiction and depression among Chinese medical students: the mediating role of sleep quality and the moderating role of peer relationships
- PMID: 35999533
- PMCID: PMC9396829
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-022-04183-9
Mobile phone addiction and depression among Chinese medical students: the mediating role of sleep quality and the moderating role of peer relationships
Abstract
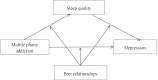
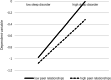
The literature has shown that mobile phone addiction is an important risk factor for depression. However, the internal mechanisms of mobile phone addiction leading to depression are still not clear. This study examined the mediating role of sleep quality and moderating role of peer relationships in the association between mobile phone addiction and depression. A sample of 450 Chinese medical students were recruited to complete measures of mobile phone addiction, depression, sleep quality and peer relationships. In this study, SPSS 25.0 and macro PROCESS were used to conduct statistical analysis on the collected data. The results showed that sleep quality partially mediated the association between mobile phone addiction and depression. Moreover, the effect of sleep quality on depression was moderated by peer relationships. The present study can advance our understanding of how and when mobile phone addiction leads to depression. Limitations and implications of this study are discussed.
Keywords: Depression; Medical students; Mobile phone addiction; Peer relationships; Sleep quality.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “Mobile Phone Addiction and Depression among Chinese Medical Students: The Mediating Role of Sleep Quality and the Moderating Role of Peer Relationship”.
Figures
References
-
- China Broadcasts The 46th statistical report on internet development in China was released. China Broadcasts. 2020;11:54.
-
- Salehan M, Negahban A. Social networking on smartphones: when mobile phones become addictive. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(6):2632–2639. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.07.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

