Physio-pathological effects of N6-methyladenosine and its therapeutic implications in leukemia
- PMID: 35999621
- PMCID: PMC9396796
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00410-3
Physio-pathological effects of N6-methyladenosine and its therapeutic implications in leukemia
Abstract
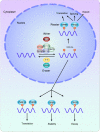
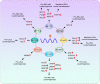
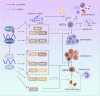
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most prevalent epigenetic modification of RNA in mammals, has become a hot topic throughout recent years. m6A is involved with every links of the RNA fate, including RNA splicing, nuclear export, translation and stability. Due to the reversible and dynamic regulatory network composed of 'writers' (methylase), 'erasers' (demethylase) and 'readers' (m6A binding proteins), m6A has been deemed as an essential modulator in vast physiological and pathological processes. Previous studies have shown that aberrant expression and dysfunction of these regulators are implicated in diverse tumors, exemplified by hematological malignancies. However, we should hold a dialectic perspective towards the influence of m6A modification on leukemogenesis. Given that m6A itself is neither pro-oncogenic nor anti-oncogenic, whether the modifications promote hematological homeostasis or malignancies occurrence and progression is dependent on the specific targets it regulates. Ample evidence supports the role of m6A in maintaining normal hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis, thereby highlighting the therapeutic potential of intervention in m6A modification process for battling leukemia. In this review, we introduce the advances of m6A modification and summarize the biological functions of m6A in RNA metabolism. Then we discuss the significance of several well-studied m6A regulators in modulating normal and malignant hematopoiesis, with focus on the therapeutic potentials of targeting these regulators for battling hematopoietic malignancies.
Keywords: Hematopoiesis; Hematopoietic stem cells; Leukemia; N6-methyladenosine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current insights on m6A RNA modification in acute leukemia: therapeutic targets and future prospects.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 12;14:1445794. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1445794. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39600630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modifications in acute myeloid leukemia.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):662-671. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae106. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38721720 Review.
-
The critical roles of m6A modification in metabolic abnormality and cardiovascular diseases.Genes Dis. 2020 Jul 31;8(6):746-758. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.011. eCollection 2021 Nov. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 34522705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversible N6-methyladenosine of RNA: The regulatory mechanisms on gene expression and implications in physiology and pathology.Genes Dis. 2020 Jul 6;7(4):585-597. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.06.011. eCollection 2020 Dec. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 33335958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine RNA modification (m6A) is of prognostic value in HPV-dependent vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Sep 1;22(1):943. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10010-x. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36050747 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of METTL14 expression in pancreatic cancer and adjacent tissues and its prognostic value for patient outcomes.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Nov 11;25(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01506-w. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39527301 Free PMC article.
-
O-GlcNAcylated FTO promotes m6A modification of SOX4 to enhance MDS/AML cell proliferation.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jan 23;23(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02058-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39849461 Free PMC article.
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in female reproductive biology and pathophysiology.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar 9;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01078-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36894952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A genotypes and prognostic signature for assessing the prognosis of patients with acute myeloid leukemia.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Aug 18;16(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01629-1. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37596597 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of FTO in regulation of gut-brain communication via Desulfovibrio fairfieldensis-produced hydrogen sulfide under arsenic exposure.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2438471. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2438471. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 39852343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Speck NA, Gilliland DG. Core-binding factors in haematopoiesis and leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:502–513. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1136–1152. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos K, Gronbaek K. Epigenetic therapy in hematological cancers. APMIS. 2019;127:316–328. - PubMed
-
- Jones PA, Issa JP, Baylin S. Targeting the cancer epigenome for therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:630–641. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

