The Remarkable Roles of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) and Its Soluble Isoforms in COVID-19: The Importance of RAGE Pathway in the Lung Injuries
- PMID: 35999871
- PMCID: PMC9387879
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-022-01081-5
The Remarkable Roles of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) and Its Soluble Isoforms in COVID-19: The Importance of RAGE Pathway in the Lung Injuries
Abstract
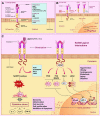
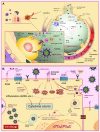
The respiratory symptoms of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients is associated with accumulation of pre-inflammatory molecules such as advanced glycation end-products (AGES), calprotectin, high mobility group box family-1 (HMGB1), cytokines, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and other molecules in the alveolar space of lungs and plasma. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGEs), which is mediated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), plays a critical role in the severity of chronic inflammatory diseases such as diabetes mellitus (DM) and ARDS. The RAGE gene is most expressed in the alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) of the pulmonary system. Several clinical trials are now being conducted to determine the possible association between the levels of soluble isoforms of RAGE (sRAGE and esRAGE) and the severity of the disease in patients with ARDS and acute lung injury (ALI). In the current article, we reviewed the most recent studies on the RAGE/ligands axis and sRAGE/esRAGE levels in acute respiratory illness, with a focus on COVID-19-associated ARDS (CARDS) patients. According to the research conducted so far, sRAGE/esRAGE measurements in patients with CARDS can be used as a powerful chemical indicator among other biomarkers for assessment of early pulmonary involvement. Furthermore, inhibiting RAGE/MAPK and Angiotensin II receptor type 1 (ATR1) in CARDS patients can be a powerful strategy for diminishing cytokine storm and severe respiratory symptoms.
Keywords: ACE2 protein; Receptor for advanced glycation end products; Respiratory distress syndrome; SARS-CoV- 2; esRAGE.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Association of Clinical Biochemists of India 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble Forms and Ligands of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Observational Prospective Study.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 14;10(8):e0135857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135857. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26274928 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of receptor for advanced glycation end-products is associated with low circulating soluble isoforms of the receptor in Type 2 diabetes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2011 Jan;120(2):81-9. doi: 10.1042/CS20100256. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011. PMID: 20726839
-
Two soluble isoforms of receptors for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in carotid atherosclerosis: the difference of soluble and endogenous secretory RAGE.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014 Nov-Dec;23(10):2540-2546. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.05.037. Epub 2014 Oct 3. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 25282185
-
Low levels of serum soluble receptors for advanced glycation end products, biomarkers for disease state: myth or reality.Int J Angiol. 2014 Mar;23(1):11-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1363423. Int J Angiol. 2014. PMID: 24627612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The receptor for advanced glycation end products and acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome.Intensive Care Med. 2012 Oct;38(10):1588-98. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2624-y. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Intensive Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22777515 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox Biomarkers - An Effective Tool for Diagnosing COVID-19 Patients and Convalescents.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr 26;17:2589-2607. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S456849. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38699594 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of nitrosative stress and glycoxidation products in the diagnosis of COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 22;14(1):9198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59876-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38649417 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of glycyrrhetinic acid glycosides against acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis.Mol Divers. 2024 Dec 2. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11058-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 39621243
-
Altered expression pattern of immune response-related genes and isoforms in hypersensitivity pneumonitis lung fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 14;14(1):24002. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74267-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39402115 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the COVID-19 Severity Hubs and Interplays in Inflammatory-Related RNA-Protein Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 6;26(9):4412. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094412. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362649 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
