Tele-Physiotherapy in Iran: Perceived Challenges by Physiotherapists to Its Implementation in COVID19 Outbreak
- PMID: 35999921
- PMCID: PMC9386775
- DOI: 10.47176/mjiri.36.17
Tele-Physiotherapy in Iran: Perceived Challenges by Physiotherapists to Its Implementation in COVID19 Outbreak
Abstract
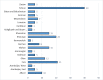
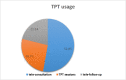
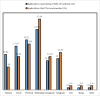
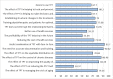
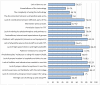
Background: COVID-19 pandemic has brought new and fundamental challenges to the healthcare system. Physiotherapists, like other rehabilitation professionals, have been involved in this crisis. One way to protect both the clients and physiotherapists from getting infected and provide physiotherapy services effectively is tele-physiotherapy (TPT). This study investigated the physiotherapists' perception of TPT and the barriers to its practical application during the COVID-19 outbreak. Methods: This cross-sectional, descriptive study was adopted in December 2020, using a newly designed checklist. The checklist had four sections, consisting of physiotherapists' knowledge and awareness, satisfaction, attitude, and also barriers to the use of TPT during the COVID-19 outbreak. The checklist was uploaded to social physiotherapy networks across Iran, and the descriptive data were analyzed statistically. Results: In this study, 192 physiotherapists participated as follows. Before the COVID-19 outbreak, 48.96% of the participants used TPT, while this rate grew to 64.06% during the outbreak. The majority of the participants (65.1%) believed that the use of TPT would improve the relationship among the physiotherapists and their patients. They also had the lowest level of knowledge (27.08%) about one item in the checklist, i.e., "how to consult with TPT". Based on the participants' views, lack of proper familiarity with the use of this method (87.5%), a lack of high-speed internet access (86.45 %), and a lack of awareness of this method and its benefits (84.37%) had the highest frequencies compared to other barriers. Conclusion: The results indicate that during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran, a significant increase in the use of TPT has developed. The overall physiotherapists' attitude towards TPT was positive, but it was necessary to minimize or eliminate the barriers to applying this effective method. Major recommendations from the participants were: continue to seek physiotherapists' and patients' perspectives, introduce proper educational programs for new students enrolled in professional associations and universities, and support the infrastructures, such as telecommunication and financial assistance from insurance companies.
Keywords: COVID-19; Physiotherapy; Rehabilitation; Tele-Physiotherapy; Tele-Rehabilitation.
© 2022 Iran University of Medical Sciences.
Similar articles
-
Physiotherapists' perceptions of and willingness to use telerehabilitation in Kuwait during the COVID-19 pandemic.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021 Apr 8;21(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12911-021-01478-x. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021. PMID: 33832473 Free PMC article.
-
Physiotherapists' behaviour, attitudes, awareness, knowledge and barriers in relation to evidence-based practice implementation in Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2017 Sep;15(3):127-141. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000106. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2017. PMID: 28399014 Free PMC article.
-
Physiotherapists' Adoption and Perceptions of Tele-Rehabilitation for Cardiorespiratory Care in Response to COVID-19.Physiother Can. 2024 May 8;76(2):211-217. doi: 10.3138/ptc-2021-0135. eCollection 2024 May. Physiother Can. 2024. PMID: 38725596 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers and facilitators of integrating physiotherapy into primary health care settings: A systematic scoping review of qualitative research.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 6;9(10):e20736. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20736. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37860510 Free PMC article.
-
Tele-Rehabilitation Interventions for Motor Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: A Narrative Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 May 26;10(6):650. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10060650. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physiotherapists' perceptions, readiness, enablers, and barriers to use telerehabilitation: A scoping review.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024;37(6):1441-1454. doi: 10.3233/BMR-240009. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38905032 Free PMC article.
-
Fall Prevention in Older Adults: Insights from Saudi Arabian Physical Therapists on the Otago Exercise Program.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 Nov 4;17:2689-2703. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S495695. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 39525679 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring physiotherapists' perceptions of telerehabilitation for musculoskeletal disorders: Insights from focus groups.Digit Health. 2024 Apr 25;10:20552076241248916. doi: 10.1177/20552076241248916. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38665882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanche S, Lin YT, Xu C, Romero-Severson E, Hengartner NW, Ke R. The novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, is highly contagious and more infectious than initially estimated. arXiv preprint arXiv:200203268. 2020.
-
- Thunström L, Newbold SC, Finnoff D, Ashworth M, Shogren JF. The benefits and costs of using social distancing to flatten the curve for COVID-19. J Benefit Cost Anal. 2020;11(2):179–95.
-
- Gourinchas PO. Flattening the pandemic and recession curves. Mitigating the COVID Economic Crisis: Act Fast and Do Whatever. CEPR 2020;31:57-62.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources