Protective antibody response to mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 vaccines in patients on maintenance haemodialysis: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 35999964
- PMCID: PMC9383598
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfac082
Protective antibody response to mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 vaccines in patients on maintenance haemodialysis: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is more frequent and severe in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on maintenance haemodialysis (HD). Vaccines are now available, but the protective response rates and determinants of humoral response to the vaccine are poorly described.
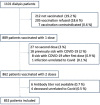
Methods: This prospective observational study describes the response rates of detectable and protective antibody titres 1 month after each dose of an mRNA vaccine in a cohort of 851 patients on maintenance HD.
Findings: Among naïve SARS-CoV-2 patients, a vast majority produced detectable (95.2%) or protective levels of antibodies (69.6%) 1 month after the second vaccine dose. In addition, the response rate was significantly higher with the mRNA-1273 than with the BNT162b2 vaccine 1 month after the second dose (79.8 versus 59.1%, respectively; P < 0.001). The main determinants for an inadequate humoral response were older age, treatment with immunosuppressants or oral anticoagulants and low serum albumin. All the patients who encountered coronavirus disease 2019 before vaccination also reached a highly protective humoral response.
Interpretation: We found an acceptable humoral response rate in patients on maintenance HD, much higher than in transplant recipients. Therefore the third dose of vaccine may be justified in those patients with an inadequate humoral response, particularly those with a history of organ transplantation or immunosuppressive treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19 mRNA vaccines; chronic kidney disease; haemodialysis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures

References
-
- COVID-19 situation update for the EU/EEA, as of 24 June 2021. [Internet]. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/cases-2019-ncov-eueea (24 June 2021, date last accessed)
-
- Scarpioni R, Manini A, Valsania Tet al. Covid-19 and its impact on nephropathic patients: the experience at Ospedale “Guglielmo da Saliceto” in Piacenza. G Ital Nefrol 2020; 37: 2020-vol2 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

