Long-Circulation and Brain Targeted Isoliquiritigenin Micelle Nanoparticles: Formation, Characterization, Tissue Distribution, Pharmacokinetics and Effects for Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 35999993
- PMCID: PMC9393037
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S368528
Long-Circulation and Brain Targeted Isoliquiritigenin Micelle Nanoparticles: Formation, Characterization, Tissue Distribution, Pharmacokinetics and Effects for Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
Purpose: We designed a novel isoliquiritigenin (ISL) loaded micelle prepared with DSPE-PEG2000 as the drug carrier modified with the brain-targeting polypeptide angiopep-2 to improve the poor water solubility and low bioavailability of ISL for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
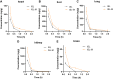
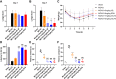
Methods: Thin film evaporation was used to synthesize the ISL micelles (ISL-M) modified with angiopep-2 as the brain targeted ligands. The morphology of the micelles was observed by the TEM. The particle size and zeta potential were measured via the nanometer particle size analyzer. The drug loading, encapsulation and in vitro release rates of micelles were detected by the HPLC. The UPLC-ESI-MS/MS methods were used to measure the ISL concentrations of ISL in plasma and main tissues after intravenous administration, and compared the pharmacokinetics and tissue distributions between ISL and ISL-M. In the MCAO mice model, the protective effects of ISL and ISL-M were confirmed via the behavioral and molecular biology experiments.
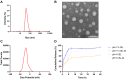
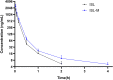
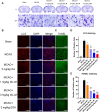
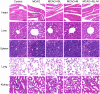
Results: The results showed that the drug loading of ISL-M was 7.63 ± 2.62%, the encapsulation efficiency was 68.17 ± 6.23%, the particle size was 40.87 ± 4.82 nm, and the zeta potential was -34.23 ± 3.35 mV. The in vitro release experiments showed that ISL-M had good sustained-release effect and pH sensitivity. Compared with ISL monomers, the ISL-M could significantly prolong the in vivo circulation time of ISL and enhance the accumulation in the brain tissues. The ISL-M could ameliorate the brain injury induced by the MCAO mice via inhibition of cellular autophagy and neuronal apoptosis. There were no the cellular structural damages and other adverse effects for ISL-M on the main tissues and organs.
Conclusion: The ISL-M could serve as a promising and ideal drug candidate for the clinical application of ISL in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
Keywords: MCAO; brain distribution; ischemic stroke; isoliquiritigenin; micelle; pharmacokinetics.
© 2022 Song et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:139–596. - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49:46–110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

