Comparison of outcomes for balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube under local vs general anesthesia
- PMID: 36000054
- PMCID: PMC9392412
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.842
Comparison of outcomes for balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube under local vs general anesthesia
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube (BDET) under local versus general anesthesia in the treatment of obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction (OETD).
Study design: Retrospective review.
Methods: Consecutive patients ages ≥18 with persistent OETD having failed adequate medical therapy underwent BDET between 2013 and 2018 under local or general anesthesia. Inclusion criteria were persistent type B or C tympanograms with symptoms or type A with symptoms upon barochallenge. Objective outcome measures were tympanometry, otoscopy and the need for additional subsequent intervention (revision dilation and tympanostomy tube). Primary outcome (failure) was defined as no change or worse in tympanogram.
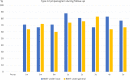
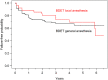
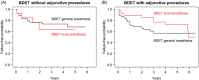
Results: The 191 patients (332 ETs), ages 18-88 years (mean 58.0) underwent BDET. The 112 patients (59%) were female. The 107 procedures (32%) were performed under local anesthesia. Mean duration of follow-up was 3.1 years (SD 1.9). Tympanograms improved to type A in 88% for BDET under local and 74% for general anesthesia at 12 months. Probability of being failure-free at 5 years was 70% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 52%-82%) in the local anesthesia group versus 65% (95% CI: 55%-73%) in the general anesthesia group. Risk of failure did not significantly differ between the groups (HR = 0.60; 95% CI: 0.27-1.31; p = .20).
Conclusion: BDET under local anesthesia is effective in treating OETD and results in sustained improvements over 2 years. The procedure was successfully performed in all but one case utilizing a precise anesthesia protocol, and results are comparable with the procedure performed under general anesthesia.
Level of evidence: 4.
Keywords: Eustachian tube; balloon dilation; in‐office balloon dilation; local anesthesia.
© 2022 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Marc Dean is a consultant for Acclarent, Aerin Medical, Biosense Webster, Immertec, Stryker, and STStent. Dr. Dennis Poe is a consultant for Acclarent.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Local Versus General Anesthesia for Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube: A Single-Center Retrospective Study in a Chinese Population.Ear Nose Throat J. 2020 May 19:145561320923172. doi: 10.1177/0145561320923172. Online ahead of print. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020. PMID: 32425122
-
In-office balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube under local anesthesia: A retrospective review.World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Oct 12;5(3):143-147. doi: 10.1016/j.wjorl.2019.08.001. eCollection 2019 Sep. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 31750426 Free PMC article.
-
Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube: 12-Month Follow-up of the Randomized Controlled Trial Treatment Group.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Apr;160(4):687-694. doi: 10.1177/0194599818821938. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 30620688 Clinical Trial.
-
In-Office Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube under Local Anesthesia.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;52(3):509-520. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 30905561 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of balloon dilation of eustachian tube in children: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Mar;154:111048. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2022.111048. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35085875
Cited by
-
In-office Eustachian tube balloon dilation under local anesthesia as a response to operating room restrictions associated with the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Surg. 2023 Apr 11;10:1033010. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1033010. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 37114150 Free PMC article.
-
Balloon Dilation Eustachian Tuboplasty Combined with Tympanotomy Tube Insertion for Treatment of Refractory Otitis Media with Effusion: A Randomized, Prospective, Controlled Trial Comparing Local Anesthesia Combined Sedation Versus General Anesthesia.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Mar 10;29:e938879. doi: 10.12659/MSM.938879. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 36895146 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Balloon dilation of the eustachian tube using endovascular balloon under local anesthesia-a case series and systematic literature review.Front Surg. 2024 Feb 20;11:1271248. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1271248. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38444902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bluestone CD, Bluestone MB. Eustachian tube: structure, function, role in otitis media. In BC Decker. Hamilton, ON; 2005; 219.
-
- Chays A, Cohen JM, Magnan J. Microfibroendoscopy of the eustachian tube. Presse Med. 1995;24(16):773‐774. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
