Durable polymer versus biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing complex percutaneous coronary intervention: a post hoc analysis of the HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS trial
- PMID: 36000257
- PMCID: PMC9743240
- DOI: 10.4244/EIJ-D-22-00372
Durable polymer versus biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing complex percutaneous coronary intervention: a post hoc analysis of the HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS trial
Abstract
Background: Comparative data of durable polymer (DP) versus biodegradable polymer (BP) drug-eluting stents (DES) are limited in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) undergoing complex percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Aims: We sought to evaluate the efficacy and safety of DP-DES and BP-DES in ACS patients receiving complex PCI.
Methods: This study was a post hoc analysis of the HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS trial. ACS patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to DP-DES or BP-DES in the HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS trial. Complex PCI was defined as having at least 1 of the following features: ≥3 stents implanted, ≥3 lesions treated, total stent length ≥60 mm, bifurcation PCI with 2 stents, left main PCI, or heavy calcification. Patient-oriented (POCO, a composite of all-cause death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and any repeat revascularisation) and device-oriented composite outcomes (DOCO, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, or target lesion revascularisation) were evaluated at 12 months.
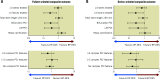
Results: Among 3,301 patients for whom full procedural data were available, 1,140 patients received complex PCI. Complex PCI was associated with higher risks of POCO and DOCO. The risks of POCO were comparable between DP-DES and BP-DES in both the complex (HR 0.87, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.57-1.33; p=0.522) and non-complex (HR 0.83, 95% CI: 0.56-1.24; p=0.368; p for interaction=0.884) PCI groups. DOCO was also not significantly different between DP-DES and BP-DES in both the complex (HR 0.74, 95% CI: 0.43-1.27; p=0.278) and non-complex (HR 0.67, 95% CI: 0.38-1.19; p=0.175; p for interaction=0.814) PCI groups.
Conclusions: In ACS patients, DP-DES and BP-DES showed similar clinical outcomes irrespective of PCI complexity.
Conflict of interest statement
H-S. Kim has received research grants or speaker's fees from Daiichi Sankyo, Boston Scientific, Terumo, Biotronik, and Dio, as well as Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Edwards Lifesciences, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim. B-K. Koo has received institutional research grants from Abbott Vascular and Philips. K. W. Park reports speaker’s fees from Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Pfizer, InnoN Pharmaceutical, DaeWoong Pharmaceutical, and JW Pharmaceutical, outside of the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to the submitted work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Long-term safety of ultrathin bioabsorbable-polymer sirolimus-eluting stents versus thin durable-polymer drug-eluting stents in acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2023 Dec;46(12):1465-1473. doi: 10.1002/clc.24139. Epub 2023 Sep 3. Clin Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37661458 Free PMC article.
-
Durable-polymer versus biodegradable-polymer drug-eluting stents in acute coronary syndromes: three-year outcomes of the HOST REDUCE POLYTECH RCT Trial.EuroIntervention. 2024 Jun 17;20(12):e750-e759. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-23-01053. EuroIntervention. 2024. PMID: 38887886 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Durable Polymer Versus Biodegradable Polymer Drug-Eluting Stents After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: The HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS Trial.Circulation. 2021 Mar 16;143(11):1081-1091. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051700. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 33205662 Clinical Trial.
-
Harmonizing Optimal Strategy for Treatment of coronary artery diseases--comparison of REDUCtion of prasugrEl dose or POLYmer TECHnology in ACS patients (HOST-REDUCE-POLYTECH-ACS RCT): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Sep 15;16:409. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0925-5. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26374625 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stents vs durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from 5 randomized trials.Am Heart J. 2021 May;235:140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2021.02.009. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Am Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33609498 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term safety of ultrathin bioabsorbable-polymer sirolimus-eluting stents versus thin durable-polymer drug-eluting stents in acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2023 Dec;46(12):1465-1473. doi: 10.1002/clc.24139. Epub 2023 Sep 3. Clin Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37661458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torii S, Jinnouchi H, Sakamoto A, Kutyna M, Cornelissen A, Kuntz S, Guo L, Mori H, Harari E, Paek KH, Fernandez R, Chahal D, Romero ME, Kolodgie FD, Gupta A, Virmani R, Finn AV. Drug-eluting coronary stents: insights from preclinical and pathology studies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17:37–51. - PubMed
-
- Byrne RA, Stone GW, Ormiston J, Kastrati A. Coronary balloon angioplasty, stents, and scaffolds. Lancet. 2017;390:781–92. - PubMed
-
- Pilgrim T, Piccolo R, Heg D, Roffi M, Tüller D, Muller O, Moarof I, Siontis GCM, Cook S, Weilenmann D, Kaiser C, Cuculi F, Hunziker L, Eberli FR, Jüni P, Windecker S. Ultrathin-strut, biodegradable-polymer, sirolimus-eluting stents versus thin-strut, durable-polymer, everolimus-eluting stents for percutaneous coronary revascularisation: 5-year outcomes of the BIOSCIENCE randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;392:737–46. - PubMed
-
- Vlachojannis GJ, Smits PC, Hofma SH, Togni M, Vazquez N, Valdés M, Voudris V, Slagboom T, Goy JJ, den Heijer, van der. Biodegradable Polymer Biolimus-Eluting Stents Versus Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stents in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: Final 5-Year Report From the COMPARE II Trial (Abluminal Biodegradable Polymer Biolimus-Eluting Stent Versus Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10:1215–21. - PubMed
-
- Raungaard B, Christiansen EH, Bøtker HE, Hansen HS, Ravkilde J, Thuesen L, Aarøe J, Villadsen AB, Terkelsen CJ, Krusell LR, Maeng M, Kristensen SD, Veien KT, Hansen KN, Junker A, Madsen M, Andersen SL, Jensen SE, Jensen LO SORT OUT VI Investigators. Comparison of Durable-Polymer Zotarolimus-Eluting and Biodegradable-Polymer Biolimus-Eluting Coronary Stents in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: 3-Year Clinical Outcomes in the Randomized SORT OUT VI Trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10:255–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

