Context-dependent CpG methylation directs cell-specific binding of transcription factor ZBTB38
- PMID: 36000449
- PMCID: PMC9665152
- DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2111135
Context-dependent CpG methylation directs cell-specific binding of transcription factor ZBTB38
Abstract
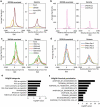
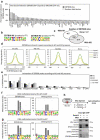
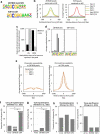
DNA methylation on CpGs regulates transcription in mammals, both by decreasing the binding of methylation-repelled factors and by increasing the binding of methylation-attracted factors. Among the latter, zinc finger proteins have the potential to bind methylated CpGs in a sequence-specific context. The protein ZBTB38 is unique in that it has two independent sets of zinc fingers, which recognize two different methylated consensus sequences in vitro. Here, we identify the binding sites of ZBTB38 in a human cell line, and show that they contain the two methylated consensus sequences identified in vitro. In addition, we show that the distribution of ZBTB38 sites is highly unusual: while 10% of the ZBTB38 sites are also bound by CTCF, the other 90% of sites reside in closed chromatin and are not bound by any of the other factors mapped in our model cell line. Finally, a third of ZBTB38 sites are found upstream of long and active CpG islands. Our work therefore validates ZBTB38 as a methyl-DNA binder in vivo and identifies its unique distribution in the genome.
Keywords: Alu repeats; DNA methylation; E2F factor; cell cycle; zinc finger protein ZBTB38.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



Similar articles
-
A family of human zinc finger proteins that bind methylated DNA and repress transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):169-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.169-181.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16354688 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into methylated DNA recognition by the C-terminal zinc fingers of the DNA reader protein ZBTB38.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 21;293(51):19835-19843. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005147. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30355731 Free PMC article.
-
The C-Terminal Zinc Fingers of ZBTB38 are Novel Selective Readers of DNA Methylation.J Mol Biol. 2018 Feb 2;430(3):258-271. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 27. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29287967
-
On how mammalian transcription factors recognize methylated DNA.Epigenetics. 2013 Feb;8(2):131-7. doi: 10.4161/epi.23632. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23324617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A common mode of recognition for methylated CpG.Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 Apr;38(4):177-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.12.005. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 23352388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kaiso mediates transcription and RNA splicing in colorectal carcinoma: role of BRCA1 in the Kaiso enhanceosome.Open Biol. 2025 Jun;15(6):240329. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240329. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Open Biol. 2025. PMID: 40460875 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age.Open Life Sci. 2024 Sep 10;19(1):20220959. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0959. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39290496 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Kaiso binding profile in clear renal cancer cells.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024 Dec 19;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00565-3. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024. PMID: 39702290 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially methylated regions associated with both liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 1;24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03149-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38302914 Free PMC article.
-
The remodeling of Z-DNA in the mammalian germ line.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Dec 16;50(6):1875-1884. doi: 10.1042/BST20221015. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 36454621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg MVC, Bourc’his D.. The diverse roles of DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:590–607. - PubMed
-
- Baubec T, Defossez P-A. Reading DNA modifications. J Mol Biol. 2020;S0022-2836(20):30096. - PubMed
-
- Fournier A, Sasai N, Nakao M, et al. The role of methyl-binding proteins in chromatin organization and epigenome maintenance. Brief Funct Genomics. 2012;11:251–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
