SERPINA5 promotes tumour cell proliferation by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway in gastric cancer
- PMID: 36000536
- PMCID: PMC9465189
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17514
SERPINA5 promotes tumour cell proliferation by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway in gastric cancer
Abstract
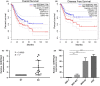
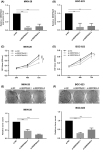
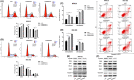
SERPINA5 belongs to the serine protease inhibitor superfamily and has been reported to be lowly expressed in a variety of malignancies. However, few report of SERPINA5 in gastric cancer has been found. The purpose of this study was to determine the role of SERPINA5 in GC and to investigate potential tumorigenic mechanisms. We performed qPCR to determine the level of SERPINA5 expression in GC. We used public databases to evaluate whether SERPINA5 could be utilized to predict overall survival and disease-free survival in GC patients. We also knocked down the expression of SERPINA5 and evaluated its effect on cell proliferation and migration. Furthermore, we explored the signal pathways and regulatory mechanisms related to SERPINA5 functions. According to our findings, SERPINA5 was shown to exhibit high expression in GC. Notably, SERPINA5 was prognostic in GC with high expression being unfavourable. SERPINA5 was further observed to promote GC tumorigenesis by modulating GC cell proliferation ability. Mechanically, SERPINA5 could inhibit CBL to regulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway, thereby promoting GC carcinogenesis progression. These results highlight the important role of SERPINA5 in GC cell proliferation and suggest that SERPINA5 could be a novel target for GC treatment and a predictor for GC prognosis.
Keywords: SERPINA5; cell proliferation; gastric cancer; signal regulation; tumour therapy.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0010882 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(3):1142-1151. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20165. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32096170
-
ACTL8 Promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer Through PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Oct;69(10):3786-3798. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08649-6. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39322809 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax toxin receptor 1/tumor endothelial marker 8 promotes gastric cancer progression through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Cancer Sci. 2020 Apr;111(4):1132-1145. doi: 10.1111/cas.14326. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31977138 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination.Development. 2016 Sep 1;143(17):3050-60. doi: 10.1242/dev.137075. Development. 2016. PMID: 27578176 Review.
-
PLC and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in disease and cancer.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25482988 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic screening of novel targets of sericin in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 5;14(1):5455. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56179-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38443583 Free PMC article.
-
[FJX1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and promotes gastric cancer proliferation via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Jun 20;43(6):975-984. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.06.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37439170 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Network pharmacology and transcriptomics reveal the mechanisms of FFBZL in the treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 11;15:1405596. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1405596. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39323640 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of HBV Integration on Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Long-Term Antiviral Therapy.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Jun 6;17:2643-2653. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S462844. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38859910 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Gastric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 3;25(3):1848. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031848. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7‐33. - PubMed
-
- Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process‐‐first American Cancer Society award lecture on cancer epidemiology and prevention. Cancer Res. 1992;52(24):6735‐6740. - PubMed
-
- He J, Zhu G, Gao L, et al. Fra‐1 is upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and affects the PI3K/Akt and p53 signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2015;47(5):1725‐1734. - PubMed
-
- Hao NB, Tang B, Wang GZ, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) upregulates heparanase expression via the PI3K/Akt/NF‐kappaB signaling pathway for gastric cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2015;361(1):57‐66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

