Is Graphene Shortening the Path toward Spinal Cord Regeneration?
- PMID: 36000717
- PMCID: PMC9776589
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c04756
Is Graphene Shortening the Path toward Spinal Cord Regeneration?
Abstract
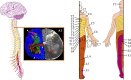
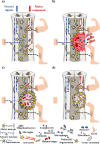
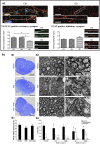
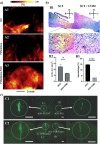
Along with the development of the next generation of biomedical platforms, the inclusion of graphene-based materials (GBMs) into therapeutics for spinal cord injury (SCI) has potential to nourish topmost neuroprotective and neuroregenerative strategies for enhancing neural structural and physiological recovery. In the context of SCI, contemplated as one of the most convoluted challenges of modern medicine, this review first provides an overview of its characteristics and pathophysiological features. Then, the most relevant ongoing clinical trials targeting SCI, including pharmaceutical, robotics/neuromodulation, and scaffolding approaches, are introduced and discussed in sequence with the most important insights brought by GBMs into each particular topic. The current role of these nanomaterials on restoring the spinal cord microenvironment after injury is critically contextualized, while proposing future concepts and desirable outputs for graphene-based technologies aiming to reach clinical significance for SCI.
Keywords: biomaterials; electrodes; glial reaction; graphene; nanocarriers; neural cells; neural stimulation; scaffolds; spinal cord injury; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

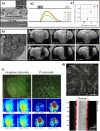
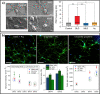
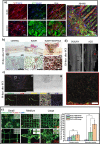
References
-
- Bierman-Duquette R. D.; Safarians G.; Huang J.; Rajput B.; Chen J. Y.; Wang Z. Z.; Seidlits S. K. Engineering Tissues of the Central Nervous System: Interfacing Conductive Biomaterials with Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, n/a, 2101577.10.1002/adhm.202101577. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

